Management and Systems Engineering
Safety, Project Management, Engineering, Management and Systems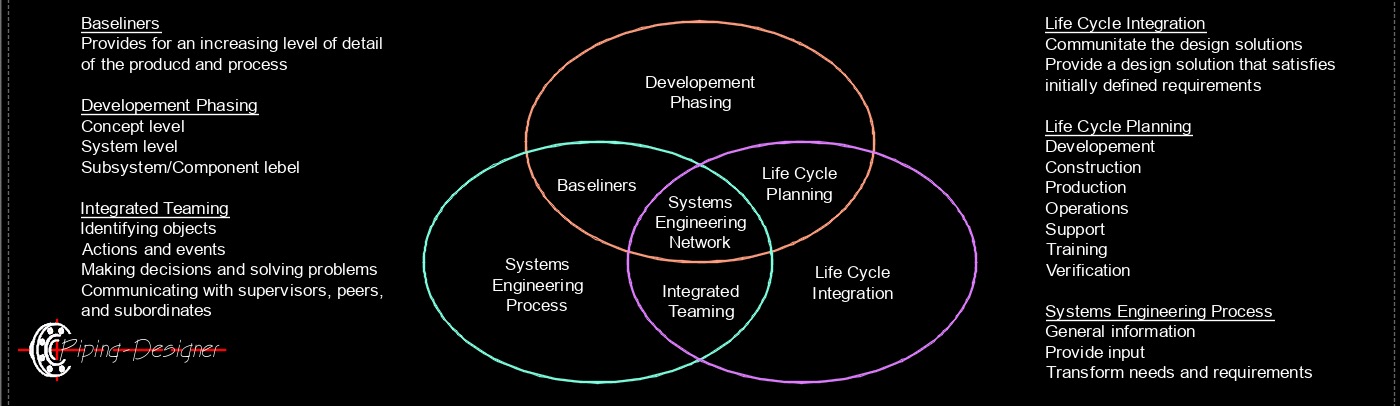
- See Article - Management and Systems Glossary
| Engineering |
| Management and Systems Engineering |
Management Engineering
Management focuses on organizing, planning, leading, and controlling resources to achieve specific objectives. It's primarily concerned with people, processes, and organizational goals.
Key Points about Management
Leadership - Motivating and guiding teams.
Planning - Defining objectives and creating strategies to achieve them.
Resource Allocation - Managing human, financial, and physical resources effectively.
Problem-Solving - Addressing operational challenges and strategic issues.
Performance Evaluation - Measuring and improving outcomes based on goals.
Common Roles
Project Manager
Operations Manager
Business Manager
Strategic Planner
Systems Engineering
Systems is an interdisciplinary approach that focuses on designing, integrating, and managing complex systems throughout their lifecycle. It deals with technical and systemic challenges to ensure the system functions as intended.
Key Points about Systems
System Design - Creating and integrating components to meet requirements.
Requirements Engineering - Defining and managing system requirements.
Lifecycle Management - Managing a system from conception to disposal.
Interdisciplinary Integration - Bridging various engineering disciplines (mechanical, electrical, software).
Risk Management - Identifying and mitigating risks in system development and operation.
Common Roles
Systems Engineer
Integration Engineer
Requirements Analyst
Lifecycle Engineer
Intersection
In fields like project management, systems engineering management, or operations, both disciplines often collaborate. Understanding both fields can enhance effectiveness in managing and delivering complex projects or systems.
Managers may oversee the development of systems, relying on Systems Engineers for technical insights.
Systems Engineers might require managerial skills to coordinate interdisciplinary teams and communicate with stakeholders.

