Shear Stress
Shear Stress Formula |
||
|
\( \tau \;=\; \dfrac{ F }{ A_c }\) (Shear Stress) \( F \;=\; \tau \cdot A_c \) \( A_c \;=\; \dfrac{ F }{ \tau }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \tau \) (Greek symbol tau) = Shear Stress | \(lbf \;/\; in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( F \) = Applied Force to the Material | \( lbf \) | \(N\) |
| \( A_c \) = Area Cross-section of Material Perpendicular to the Applied Force | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
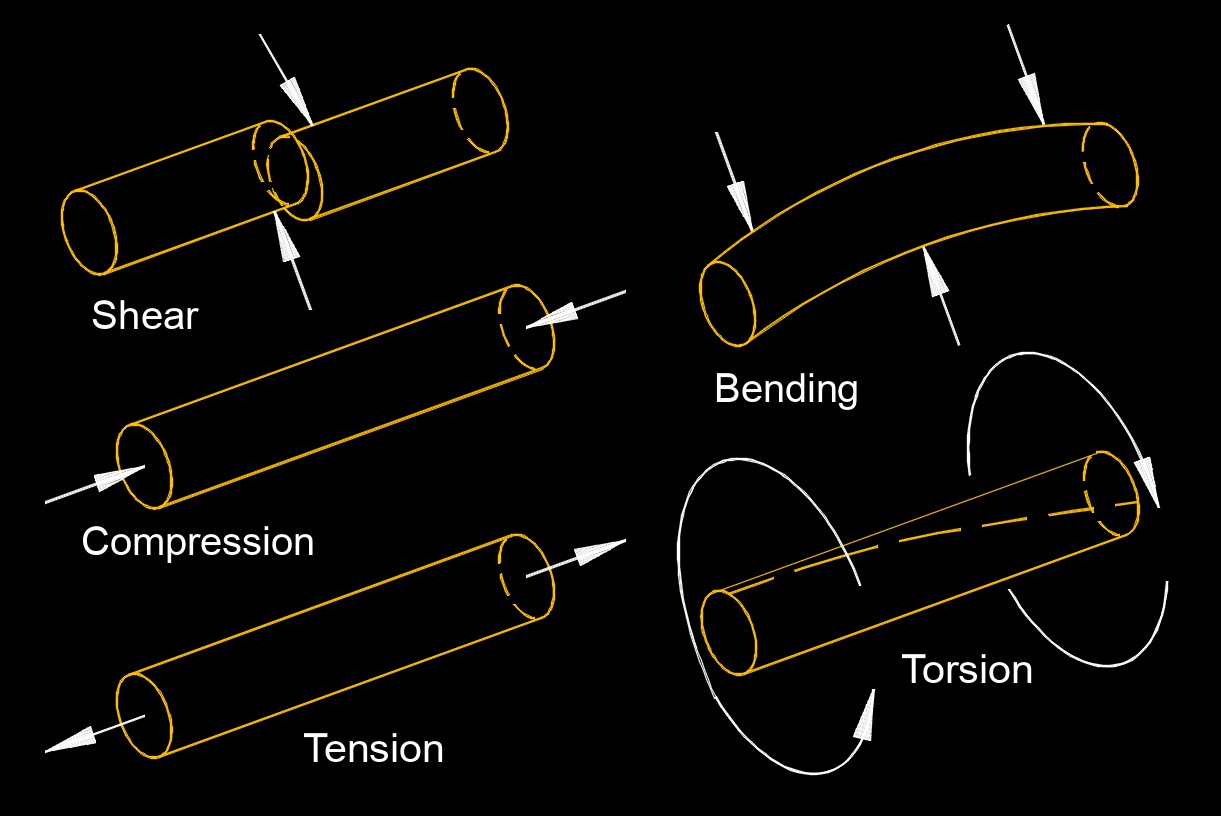
Shear stress, abbreviated as \(\tau\) (Greek symbol tau), also called tangential sheer or shearing stress, is a mechanical property that describes the force per unit area acting parallel to the surface of a material, causing it to deform by sliding or shearing one portion relative to another. It arises when a force is applied tangentially to a surface, such as when layers of a material slide past each other or when a fluid flows over a solid boundary.
Different materials have different responses to shear stress. Some materials, such as fluids, exhibit continuous deformation when subjected to shear stress and are called "shear-thinning" materials. Others, like solids, have a more rigid response and resist deformation.
This type of stress is used in understanding the behavior of materials under various conditions, such as in structural components like beams, where shear stress can lead to failure if it exceeds the material’s strength. It also plays a key role in fluid dynamics, where shear stress influences viscosity and flow behavior, as seen in the interaction between a fluid and a pipe’s inner surface. Unlike normal stress, which acts perpendicularly to a surface (causing compression or tension), shear stress is unique in its lateral action, making it essential for designing stable structures and analyzing material deformation.

