Air Resistance
Air Resistance Formula |
||
|
Equation 1 - \( F_a \;=\; k \cdot v^2 \) (Air Resistance) Equation 2 - \( F_a \;=\; \dfrac{ \rho \cdot C_d \cdot A }{ 2 } \cdot v^2 \)
|
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( F_a \) = force of air resistance or drag | \( lbf \) | \(N\) |
| \( k \) = a constant that collects the effects of area, density, and drag | \(lbm \;/\; ft^3\) | \(kg \;/\; m^3\) |
| \( v \) = velocity of the moving object | \(ft \;/\; sec\) | \(m \;/\; s\) |
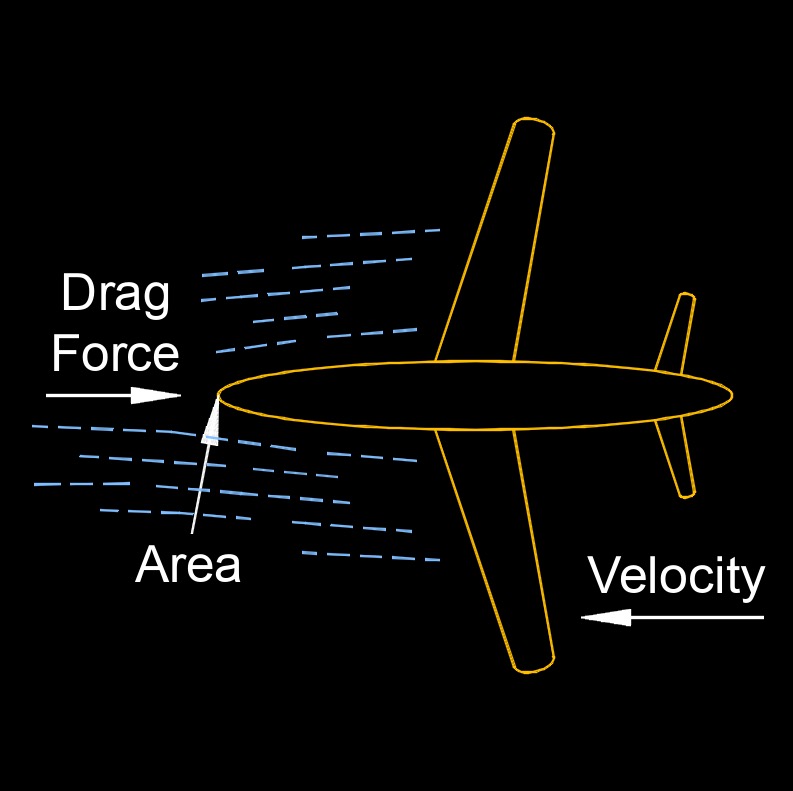 Air resistance, abbreviated as \(F_a\), also known as aerodynamic drag or air drag, is a force that opposes the motion of an object through the air. It is caused by the friction and pressure differences between the air molecules and the surface of the object. Air resistance is present in all forms of motion that involve objects moving through the air, including vehicles, aircraft, and even human movement such as running or cycling.
Air resistance, abbreviated as \(F_a\), also known as aerodynamic drag or air drag, is a force that opposes the motion of an object through the air. It is caused by the friction and pressure differences between the air molecules and the surface of the object. Air resistance is present in all forms of motion that involve objects moving through the air, including vehicles, aircraft, and even human movement such as running or cycling.
The magnitude of air resistance depends on several factors, including the speed and direction of the object's motion, the size and shape of the object, and the density and viscosity of the air. Air resistance increases as the object's speed increases and as its size and surface area increase. Streamlined objects with smooth, curved surfaces create less air resistance than objects with flat or rough surfaces.
Air resistance can have a significant impact on the performance and fuel efficiency of vehicles and aircraft. Engineers and designers use various techniques to reduce air resistance, including streamlining the body and adding features such as spoilers, air dams, and airfoils to control the airflow around the object. Reducing air resistance can improve the speed, fuel efficiency, and stability of vehicles and aircraft, and is an important consideration in many fields, including transportation, sports, and aerospace engineering.

