Angular Velocity
Angular Velocity Formula |
||
|
\( \omega \;=\; \dfrac{ \Delta \theta }{ \Delta t }\) (Angular Velocity) \( \Delta \theta \;=\; \omega \cdot \Delta t \) \( \Delta t \;=\; \dfrac{ \Delta \theta }{ \omega }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \omega \) (Greek symbol omega) = Angular Velocity | \(deg \;/\; sec\) | \(rad \;/\; s\) |
| \( \Delta \theta \) (Greek symbol theta) = Change in Angular Displacement | \(deg\) | \(rad\) |
| \( \Delta t \) = Change in Time | \(sec\) | \(s\) |
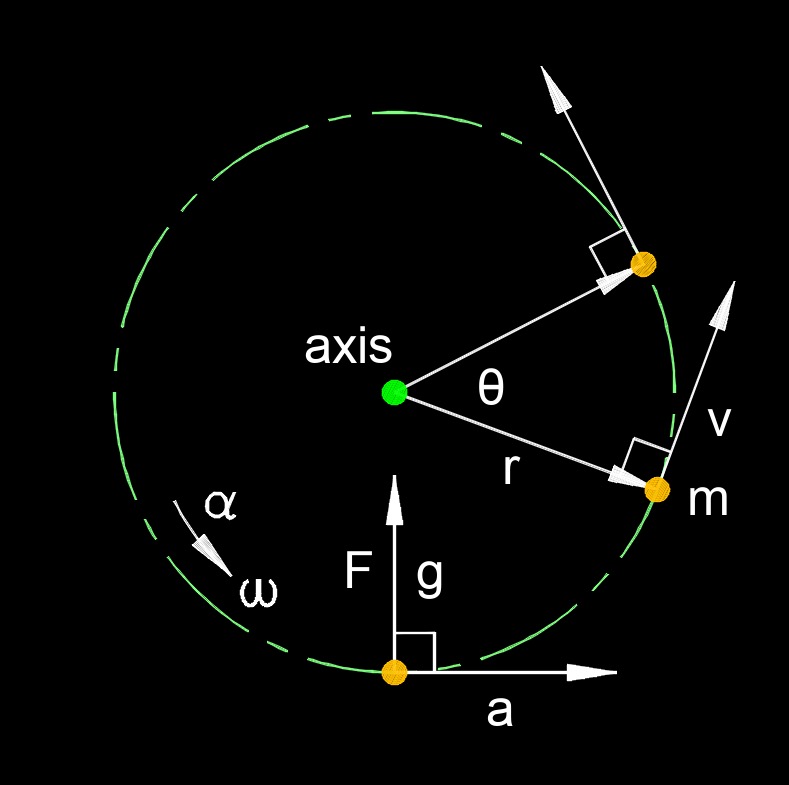
Angular velocity, abbreviated as \(\omega\) (Greek symbol omega), also called angular speed, is a vector quantity that represents the rate of change of angular displacement with respect to time. In other terms, it measures how quickly an object is rotating or spinning around an axis. Angular velocity is a crucial concept in physics and engineering, particularly in the study of rotational motion. It describes how fast an object is rotating or how quickly it is changing its angular position. In many cases, it's used in conjunction with linear velocity to analyze the motion of objects that are both translating and rotating simultaneously.

