Electromagnetism
Physics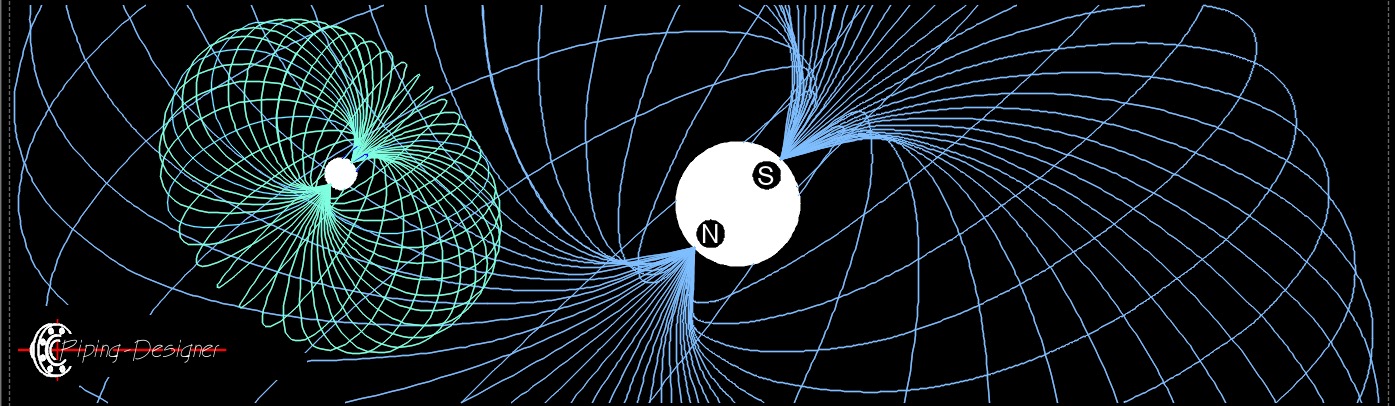 Electromagnetism is the branch of physics that deals with the study of electric and magnetic fields and their interactions with charged particles and currents. It is one of the four fundamental forces of nature and is responsible for the behavior of electromagnetic waves, which include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. The electric and magnetic fields are intimately related to each other and are described by Maxwell's equations, which provide a unified description of electric and magnetic phenomena. These equations show that a changing electric field produces a magnetic field, and vice versa. When these fields oscillate in time, they produce electromagnetic waves that propagate through space at the speed of light.
Electromagnetism is the branch of physics that deals with the study of electric and magnetic fields and their interactions with charged particles and currents. It is one of the four fundamental forces of nature and is responsible for the behavior of electromagnetic waves, which include radio waves, microwaves, infrared radiation, visible light, ultraviolet radiation, X-rays, and gamma rays. The electric and magnetic fields are intimately related to each other and are described by Maxwell's equations, which provide a unified description of electric and magnetic phenomena. These equations show that a changing electric field produces a magnetic field, and vice versa. When these fields oscillate in time, they produce electromagnetic waves that propagate through space at the speed of light.
| Physics |
Electromagnetism has numerous applications in modern technology, including telecommunications, electronics, electric power generation and transmission, and medical imaging, among others. It is also fundamental to our understanding of the behavior of matter at the atomic and subatomic level and plays a crucial role in modern physics, including the study of quantum mechanics and the theory of relativity.
- See Articles - List of Tags / List of Categories / List of Articles / List of Glossaries / Nomenclature and Symbols / (See Electromagnetism Glossary)
Electromagnetism Fundamental Forces
Electromagnetism is one of the four fundamental forces of nature, governing the interactions between electrically charged particles and electric fields. It encompasses both electric and magnetic forces, which are unified into a single force described by Maxwell’s equations. The electric force manifests between charged particles, where like charges repel and opposite charges attract, with its strength governed by Coulomb’s Law. The magnetic force, on the other hand, acts on moving charges or current-carrying conductors in the presence of a magnetic field, as described by the Lorentz Force Law. These forces are interconnected, as changing electric fields can generate magnetic fields and vice versa, enabling phenomena like electromagnetic waves, such as light and radio waves, which propagate through space at the speed of light. Mediated by photons, the electromagnetic force has an infinite range, though its strength diminishes with the square of the distance. This force is vastly stronger than gravity but weaker than the strong nuclear force, playing a critical role in everyday phenomena like electricity, magnetism, chemical bonding, and the behavior of atoms and molecules. In the quantum realm, electromagnetism is described by Quantum Electrodynamics (QED), a precise framework that underpins much of modern physics.

