Compression Spring
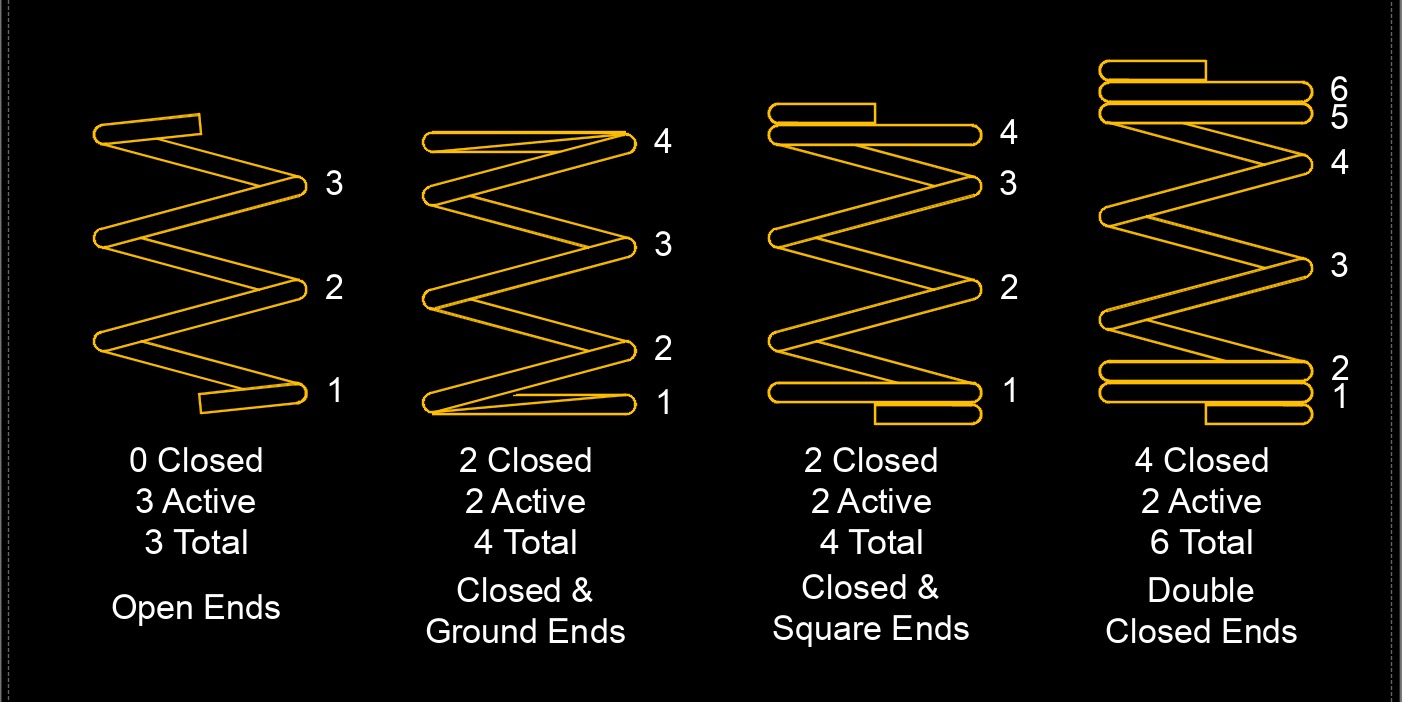
 Compression spring is a mechanical device designed to store and release mechanical energy. It is a type of helical spring, meaning it is made up of a tightly wound coil of wire with a constant diameter. Compression springs are widely used in various industries and applications. The primary function of a compression spring is to exert a force when it is compressed. When an external force is applied to the ends of the spring, it compresses and absorbs the energy, storing it within the spring. When the external force is released or removed, the spring expands and releases the stored energy, exerting a force in the opposite direction.
Compression spring is a mechanical device designed to store and release mechanical energy. It is a type of helical spring, meaning it is made up of a tightly wound coil of wire with a constant diameter. Compression springs are widely used in various industries and applications. The primary function of a compression spring is to exert a force when it is compressed. When an external force is applied to the ends of the spring, it compresses and absorbs the energy, storing it within the spring. When the external force is released or removed, the spring expands and releases the stored energy, exerting a force in the opposite direction.
Compression springs are available in a wide range of sizes, materials, and designs to suit different requirements. The choice of material depends on factors such as desired strength, temperature resistance, corrosion resistance, and cost. Common materials used for compression springs include steel alloys, stainless steel, and various non-ferrous alloys. It's important to note that while compression springs are typically designed to operate in a linear fashion, they can also be designed for specific applications where they may have a non-linear force deflection characteristic or have other unique properties based on the design requirements.

