Borda-Carnot Equation
Borda-Carnot Equation |
||
|
\( \Delta E \;=\; \dfrac{1}{ 2 } \cdot \epsilon \cdot \rho \cdot \left( {v_1 - v_2} \right)^2 \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \Delta E \) = Fluid Mechanical Energy Loss | \( lbf-ft \) | \(J\) |
| \( \epsilon \) (Greek symbol epsilon) = Empirical Loss Coefficient | \( dimensionless \) | \( dimensionless \) |
| \( \rho \) (Greek symbol rho) = Fluid Density | \(lbm\;/\;ft^3\) | \(kg\;/\;m^3\) |
| \( v_1 \) = Mean Flow Velocity before Expansion | \(ft\;/\;sec\) | \(m\;/\;s\) |
| \( v_2 \) = Mean Flow Velocity after Expansion | \(ft\;/\;sec\) | \(m\;/\;s\) |
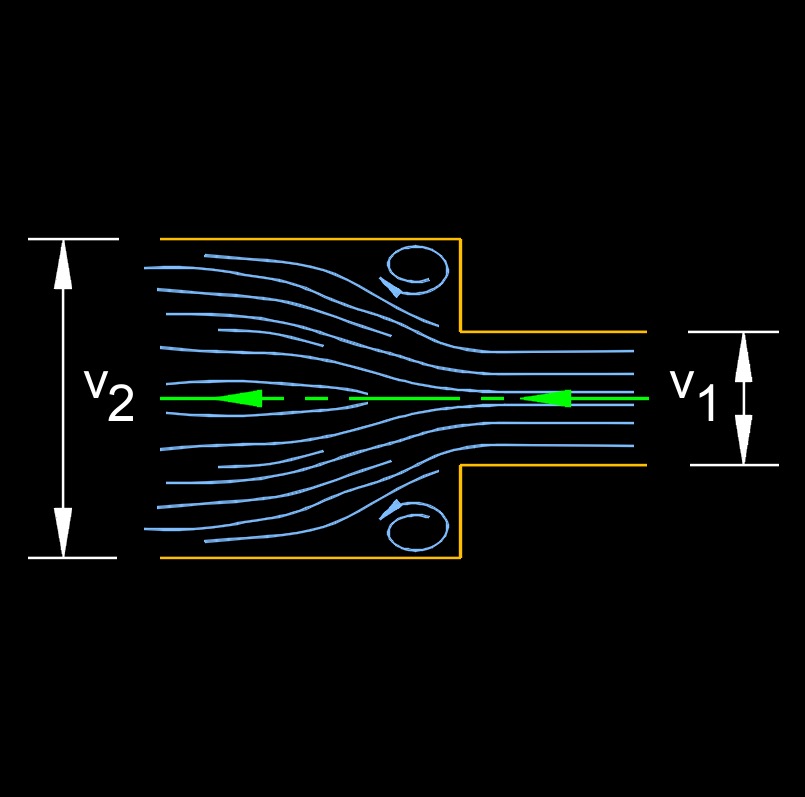
Borda-Carnot equation is a empirical description of the mechanical loss energy losses of the fluid due to a sudden flow expansion. It describes how the total head losses due to the expansion. This equation is only valid for expansion, in the case of a contraction, the Borda-Carnot Equation cannot be used as it would indicate that energy is created. The empirical loss coefficient, \(\large{\epsilon}\), is a number between 0 and 1. For an abrupt and wide expansion, \(\large{\epsilon}\) is equal to 1. For other instances, the value should be determined through empirical means.

