Fluid
Fluid Properties |
|||
| Properties | Gas | Liquid | Solid |
| Compressibility | Yes | Low | No |
| Density | Low | Moderate | High |
| Expandability | Yes | Yes | No |
| Intermolecule force strength | Weak | Moderate | Strong |
| Particle Movement | Free movement | Free movement | No free movement |
| Shape | Infinite | Infinite | Fixed |
| Shear Resistance | Yes | Yes | No |
| Viscosity | Low | Varies | No |
| Volume | Infinite | Fixed | Fixed |
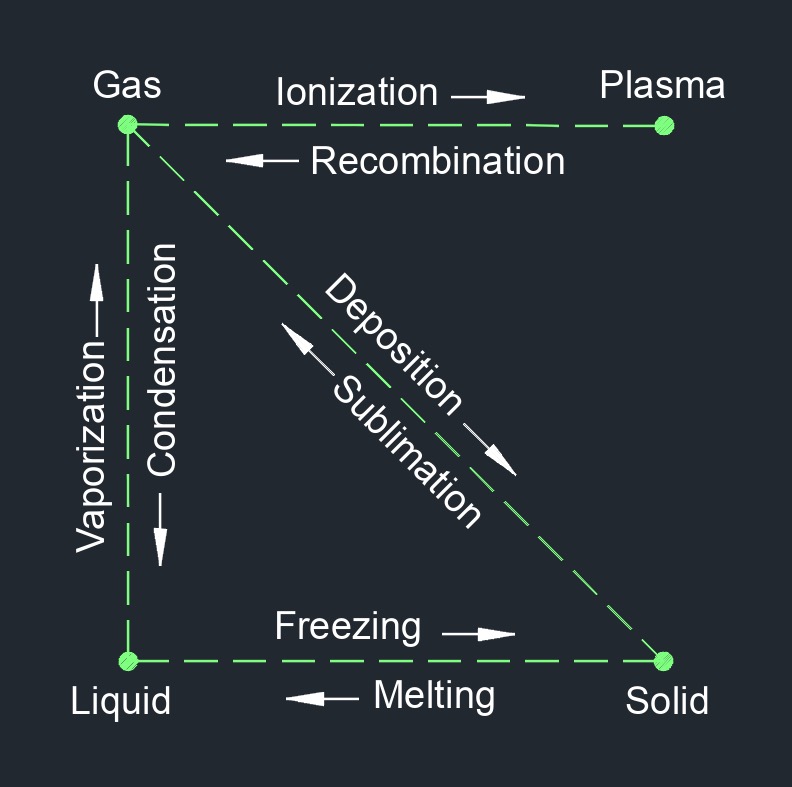 Fluid is a substance that deforms and changes position when put under stress. Fluids can be both liquids and gases. They are distinguished from solids, which have a definite shape and volume. Fluids are essential in various fields, including physics, engineering, and biology. Understanding fluid behavior is crucial for designing systems such as pipelines, pumps, hydraulic systems, and aerodynamic devices. Fluid dynamics, the study of how fluids behave under different conditions, is a fundamental branch of physics and engineering that deals with the properties and motion of fluids.
Fluid is a substance that deforms and changes position when put under stress. Fluids can be both liquids and gases. They are distinguished from solids, which have a definite shape and volume. Fluids are essential in various fields, including physics, engineering, and biology. Understanding fluid behavior is crucial for designing systems such as pipelines, pumps, hydraulic systems, and aerodynamic devices. Fluid dynamics, the study of how fluids behave under different conditions, is a fundamental branch of physics and engineering that deals with the properties and motion of fluids.
Fluid Types
Compressibility Fluid - When the density of the fluid changes with the application of external force.
Ideal Fluid - This assumes to have no viscosity, meaning no resistance or shear, and not compressable. In an ideal fluids there is uniform velocity distribution when flowing.
Ideal Plastic Fluid - A fluid, in which shear stress is more than the yield value and shear stress is directly proportional to the rate of shear strain.
Incompressibility Fluid - When the density of the fluid doesn’t change with the application of external force.
Newtonian Fluid - This fluid's viscosity is constant no matter how much shear is applied for a constant temperature.
Non-Newtonian Fluid - This is the opposite of Newtonian fluids and does not following Newton's law of viscosity. These fluids having variable viscosity when shear is applied.
Real Fluid - This fluid does not have uniform velocity distribution, it is compressable, shows finite viscosities and experience friction and turbulance in flow.

