Head Loss
Major Head Loss Formula
|
||
|
\( h_l \;=\; f \cdot \dfrac{ l }{ d } \cdot \dfrac{ v^2 }{ 2 \cdot g } \) (Major Head Loss) \( f \;=\; \dfrac{ 2 \cdot g \cdot h_l \cdot d }{ l \cdot v^2 }\) \( l \;=\; \dfrac{ 2 \cdot g \cdot h_l \cdot d }{ f \cdot v^2 }\) \( d \;=\; \dfrac{ l \cdot f \cdot v^2 }{ 2 \cdot g \cdot h_l }\) \( v \;=\; \sqrt{ \dfrac{ g \cdot h_l \cdot d }{ f \cdot l } } \) \( g \;=\; \dfrac{ f \cdot h_l \cdot d }{ 2 \cdot l \cdot v^2 }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( h_{l-major} \) = Major Head Loss | \( ft \) | \( m \) |
| \( f \) = Friction Factor | \(dimensionless \) | \(dimensionless \) |
| \( l \) = Pipe Lenght | \( ft \) | \( m \) |
| \( d \) = Pipe Inside Diameter | \( in \) | \( mm \) |
| \( v \) = Flow Velocity | \(ft\;/\;sec\) | \(m\;/\;s\) |
| \( g \) = Gravitational Constant | \(lbf-ft^2\;/\;lbm^2\) | \(N - m^2\;/\;kg^2\) |
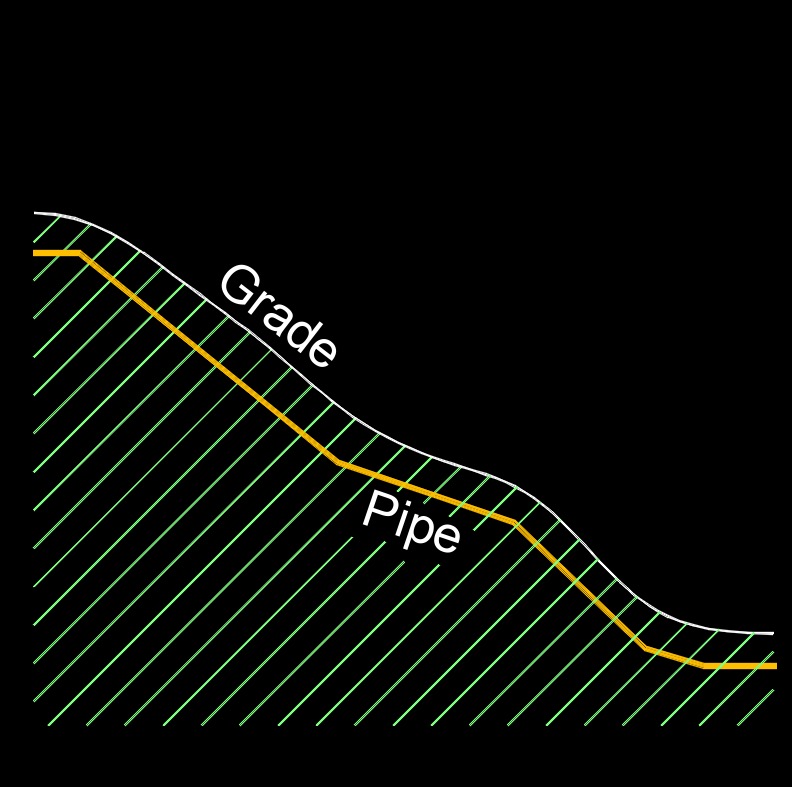
Head loss, abbreviated as \(h_l\), is a pressure loss due to the resistance of the fluid and obstructions along the way in a pipe. In fluid dynamics, head loss refers to the reduction in total head (pressure energy, kinetic energy, and potential energy) of a fluid as it flows through a pipe or other conduit due to friction between the fluid and the surface of the conduit. This head loss is also known as friction loss, and it is measured in units of length, such as feet or meters. The head loss increases with the flow rate of the fluid, the length and diameter of the conduit, and the roughness of the conduit surface. It is an important consideration in the design and operation of fluid transport systems, as it can affect the efficiency of the system and the required pump or compressor power.
Understanding and quantifying these factors are essential for engineers and designers to optimize the performance and efficiency of fluid systems and pipelines. Computational tools and empirical formulas, such as the Darcy-Weisbach equation or the Hazen-Williams equation, are commonly used to estimate head loss in practical engineering applications.
Minor Head Loss Formula
|
||
|
\( h_l \;=\; K \cdot dfrac{ v^2 }{ 2 \cdot g }\) (Minor Head Loss) \( K \;=\; \dfrac{ 2 \cdot g \cdot h_l }{ v^2 }\) \( v \;=\; \sqrt{ 2 \cdot g \cdot h_l } \) \( g \;=\; \dfrac{ v^2 }{ 2 \cdot h_l }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \(\large{ h_{l-minor} }\) = Minor Head Loss | \( ft \) | \( m \) |
| \(\large{ K }\) = Loss Coefficient | \(dimensionless \) | \(dimensionless \) |
| \(\large{ v }\) = Flow Velocity | \(ft\;/\;sec\) | \(m\;/\;s\) |
| \(\large{ g }\) = Gravitational Constant | \(lbf-ft^2\;/\;lbm^2\) | \(N - m^2\;/\;kg^2\) |
Major Factors Affecting Head Loss
Several factors contribute to head loss, and understanding these factors is crucial in designing and analyzing fluid systems.
Frictional Resistance - Friction between the fluid and the walls of the conduit causes a loss of energy. The roughness of the pipe or duct surface, as well as the velocity and viscosity of the fluid, influence frictional resistance.
Pipe Length - Longer pipes result in higher head loss due to the increased distance over which frictional losses occur.
Pipe Diameter - Smaller diameter pipes generally have higher frictional losses because a larger proportion of the fluid comes into contact with the pipe walls.
Flow Velocity - Higher flow velocities lead to increased head loss due to greater frictional resistance. However, very low velocities can also result in increased head loss due to a different phenomenon called laminar flow.
Pipe Roughness - The roughness of the internal surface of the pipe affects frictional losses. Smoother pipes generally have lower head losses.
Fluid Viscosity - Viscous fluids experience greater frictional losses. The viscosity of the fluid is a crucial factor, especially in systems where the fluid properties can vary.
Changes in Elevation - Changes in the elevation of the fluid column result in potential energy changes, affecting the total head. Changes in elevation can lead to either a gain or loss of head.
Fittings and Valves - The presence of fittings, valves, elbows, and other components in the fluid path introduces additional sources of head loss due to changes in flow direction.
Flow Regime - The type of flow, whether laminar or turbulent, affects head loss differently. In general, turbulent flow has higher head loss compared to laminar flow for the same flow rate.
Fluid Density - Although it has a smaller impact compared to other factors, changes in fluid density can affect head loss, especially in systems where temperature changes significantly.

