Matter
Matter Properties |
|||
| Properties | Gas | Liquid | Solid |
| Compressibility | Yes | Low | No |
| Density | Low | Moderate | High |
| Expandability | Yes | Yes | No |
| Intermolecule force strength | Weak | Moderate | Strong |
| Particle Movement | Free movement | Free movement | No free movement |
| Shape | Infinite | Infinite | Fixed |
| Shear Resistance | Yes | Yes | No |
| Viscosity | Low | Varies | No |
| Volume | Infinite | Fixed | Fixed |
 When you look around, everything you see or may not see in the universe is made up of matter. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. This includes all physical substances and objects that we can see, touch, and interact with.
When you look around, everything you see or may not see in the universe is made up of matter. Matter is anything that has mass and takes up space. This includes all physical substances and objects that we can see, touch, and interact with.
Matter can exist in different states or phases, such as solid, liquid, gas, or plasma, depending on the temperature and pressure conditions. Matter is composed of atoms, which are the basic building blocks of all matter. Atoms are made up of protons, neutrons, and electrons, which are subatomic particles with different properties and charges. The properties of matter, such as its density, melting point, and chemical reactivity, depend on the arrangement and behavior of these subatomic particles.
Almost all matter is composed of an electric charge. All electric charges are either positive or negative. Like charges repel each other, unlike charges attract each other. Matter that has no overall charge is called neutral. Matter is essential to our everyday lives and to many scientific disciplines, such as chemistry, physics, and materials science. Understanding the properties and behavior of matter is important for developing new technologies, improving materials and products, and addressing environmental and health issues.
Matter Types
- Gas - Able to be compressed to fit a confined space and expanded when released.
- Liquid - A specific volume and can hold any shape it is contained within.
- Plasma - It is everywhere in the universe and the most common of all matter. Of all types of matter it is closest to a gas.
- Solid - Has particles that are compressed together in an orderly pattern.
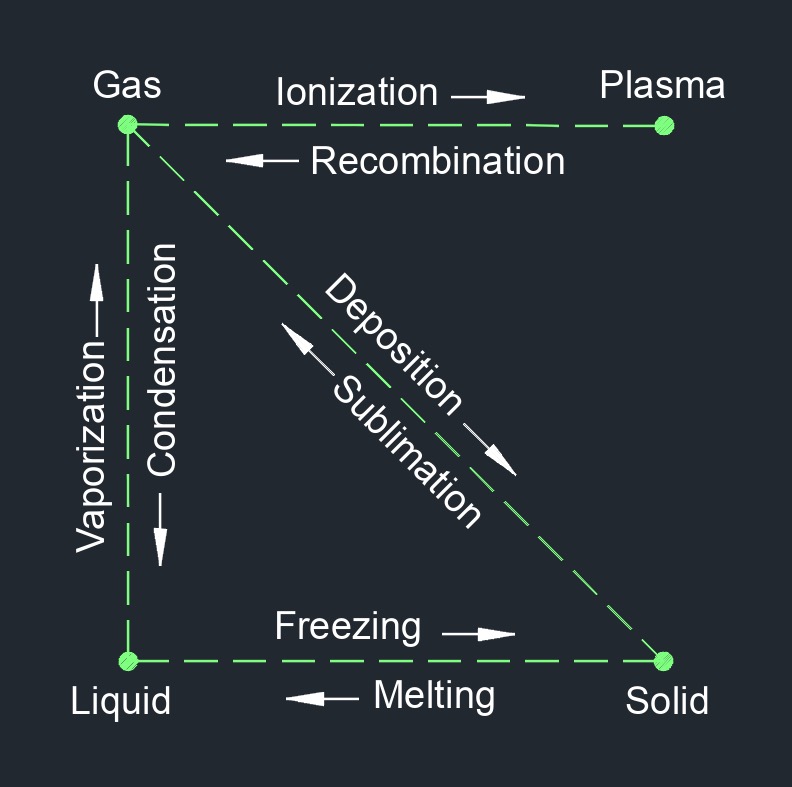 Matter Transition Phases
Matter Transition Phases
Matter can exist in different phases or states, which are characterized by the arrangement and behavior of its particles (atoms, molecules, or ions). The four primary phases of matter are:
Solid - In a solid, particles are closely packed together, and they vibrate in fixed positions. Solids have a definite shape and volume.
Liquid - In a liquid, particles are still close together, but they have more freedom to move than in a solid. Liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container.
Gas - In a gas, particles are widely spaced and have high kinetic energy. Gases have neither a definite shape nor volume and will expand to fill any container.
Plasma - Plasma is a unique phase of matter that occurs at extremely high temperatures or in the presence of intense energy, such as in stars, lightning, or some laboratory conditions.
Matter Transition Phase Change | |
|---|---|
| Phase Change | Name |
| gas to liquid | condensation |
| gas to solid | deposition |
| liquid to solid | freezing |
| gas to plasma | ionization |
| solid to liquid | melting |
| plasma to gas | recombination |
| solid to gas | sublimation |
| liquid to gas | vaporization |
 Matter Transition Phases
Matter Transition Phases
Matter can exist in different phases or states, which are characterized by the arrangement and behavior of its particles (atoms, molecules, or ions). The four primary phases of matter are:
Solid - In a solid, particles are closely packed together, and they vibrate in fixed positions. Solids have a definite shape and volume.
Liquid - In a liquid, particles are still close together, but they have more freedom to move than in a solid. Liquids have a definite volume but take the shape of their container.
Gas - In a gas, particles are widely spaced and have high kinetic energy. Gases have neither a definite shape nor volume and will expand to fill any container.
Plasma - Plasma is a unique phase of matter that occurs at extremely high temperatures or in the presence of intense energy, such as in stars, lightning, or some laboratory conditions.
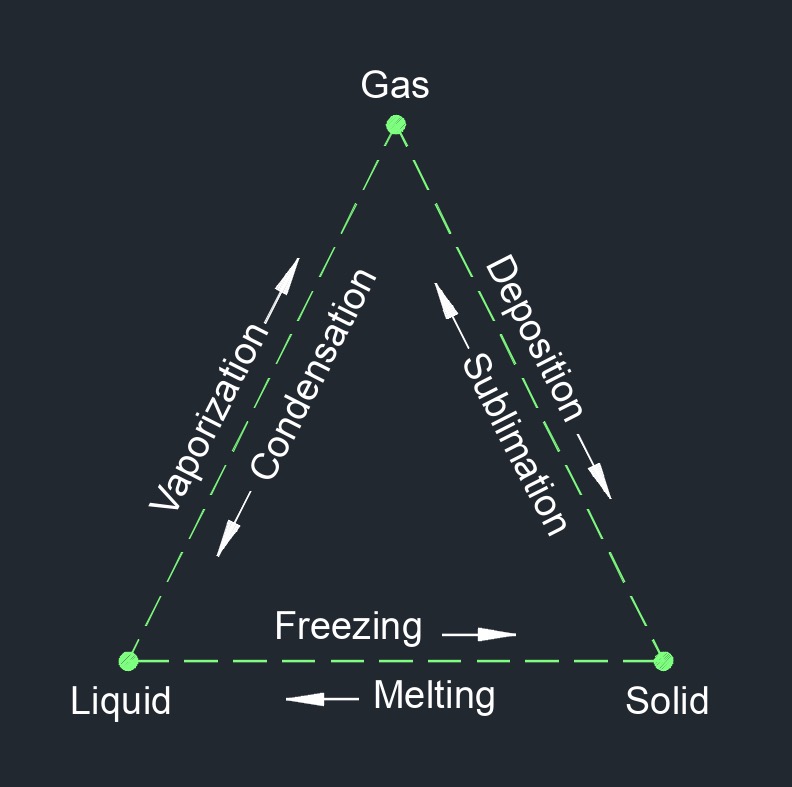 Enthalpy of a System
Enthalpy of a System
The chart to the right shows the transitional phase change between gas, liquid, an solid. Gas having the highest enthalpy, liquid having intermediate enthalpy, and liquid having the lowest enthalpy. The enthalpy of a system is a thermodynamic property that combines the internal energy of the system with the product of its pressure and volume. It is often used in thermodynamics to describe and analyze processes involving heat transfer at constant pressure. Enthalpy is particularly useful for open systems or systems that exchange energy with their surroundings through heat transfer.
Enthalpy is a state function, which means that it depends only on the initial and final states of the system and is independent of the specific path taken to reach those states.
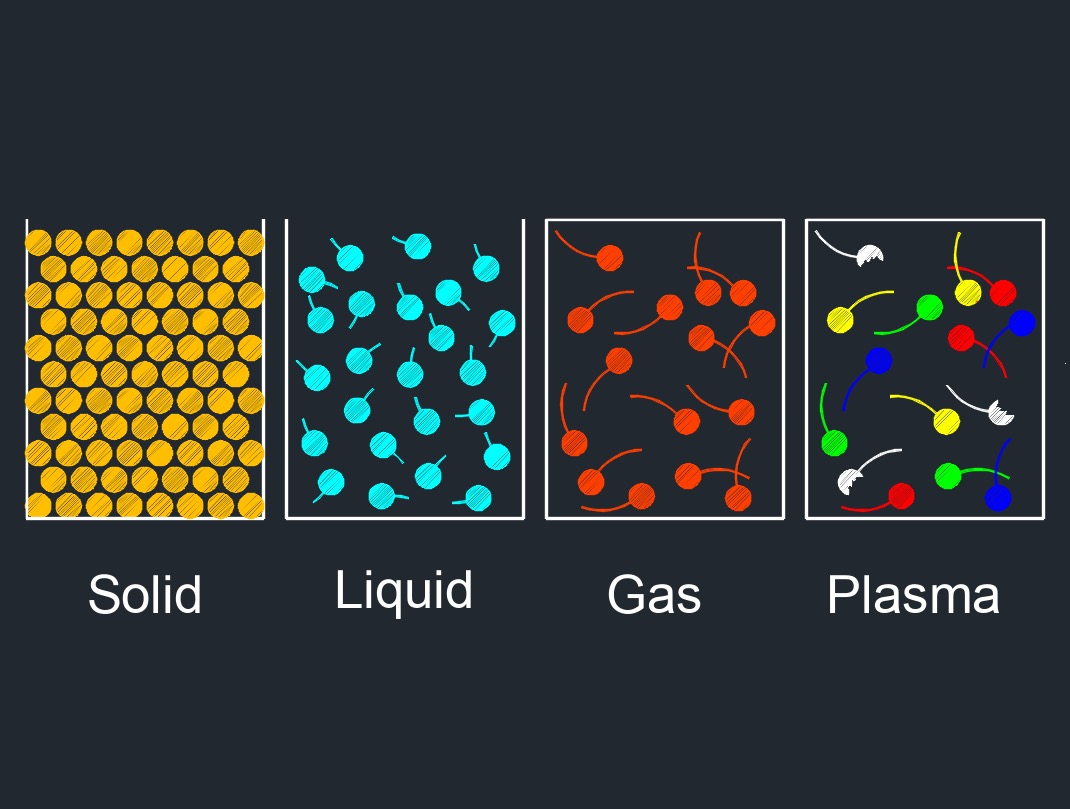 Phase to Phase Transition
Phase to Phase Transition
This diagram shows the arrangement of the physical properties between solids, liquids, and gas. Phase transitions are physical changes that occur when a substance transitions from one phase of matter to another. The most common phases of matter are solid, liquid, and gas, but there are other phases, such as plasma and Bose-Einstein condensates, that occur under specific conditions. Phase transitions can be classified into different categories based on the change in the substance's properties. Here are some common phase-to-phase transitions:
Melting (Solid to Liquid) - This transition occurs when a solid substance absorbs enough heat energy to overcome the forces holding its particles (atoms, molecules, or ions) in a fixed, ordered lattice structure. As a result, the substance becomes a liquid.
Freezing (Liquid to Solid) - The reverse of melting, freezing happens when a liquid loses enough heat energy to form a solid structure with its particles arranged in an ordered manner.
Vaporization (Liquid to Gas) - Vaporization occurs when a liquid is heated to a temperature where the kinetic energy of its particles overcomes the forces of attraction between them, causing the substance to become a gas.
Condensation (Gas to Liquid) - This phase transition is the reverse of vaporization. It happens when a gas loses heat energy and its particles come closer together to form a liquid.
Sublimation (Solid to Gas) - Sublimation occurs when a solid directly transitions into a gas without passing through the liquid phase. It typically happens at specific temperature and pressure conditions.
Deposition (Gas to Solid) - Deposition is the reverse of sublimation, where a gas transitions directly into a solid without passing through the liquid phase.

