Beam Bending Stress
Beam Bending Stress Formula |
||
|
\( \sigma_b \;=\; \dfrac{ M \cdot y}{I }\) (Beam Bending Stress) \( M \;=\; \dfrac{ \sigma_b \cdot I}{y }\) \( y \;=\; \dfrac{ \sigma_b \cdot I}{M }\) \( I \;=\; \dfrac{ M \cdot y}{ \sigma_b }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \sigma_b \) (Greek symbol sigma) = Bending Stress | \(lbf\;/\;in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( M \) = Moment about the Neutral Axis | \(lbf\;/\;sec\) | \(kg-m\;/\;s\) |
| \( y \) = Perpendicular Distance to the Neutral Axis | \(in\) | \(mm\) |
| \( I \) = Second Moment of Area about the Neutral Axis (Moment of Inertia) | \(in^4\) | \(mm^4\) |
 Beam bending stress, abbreviated as \(\sigma \) (Greek symbol sigma), also called flexure, flexural stress or bending moment stress, is when a beam is subjected to a load along it's length axis with stress applied perpendicular to the axis. It is the internal stress induced in a beam when subjected to bending loads. When a beam is loaded in such a way that it causes it to bend, different parts of the beam experience varying levels of stress.
Beam bending stress, abbreviated as \(\sigma \) (Greek symbol sigma), also called flexure, flexural stress or bending moment stress, is when a beam is subjected to a load along it's length axis with stress applied perpendicular to the axis. It is the internal stress induced in a beam when subjected to bending loads. When a beam is loaded in such a way that it causes it to bend, different parts of the beam experience varying levels of stress.
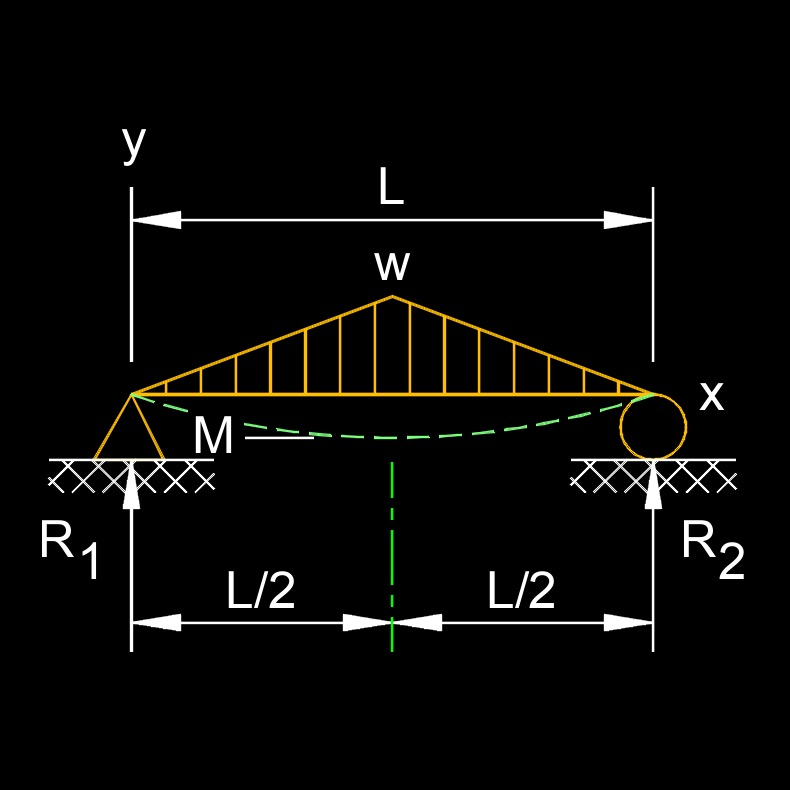 Bending stress is highest at the top and bottom surfaces of the beam, known as the tension and compression zones, respectively. These zones are located farthest from the neutral axis of the beam, which is an imaginary line that divides the beam into equal top and bottom portions. The magnitude of bending stress in a beam is directly proportional to the applied bending moment and inversely proportional to the moment of inertia of the beam's cross-sectional shape.
Bending stress is highest at the top and bottom surfaces of the beam, known as the tension and compression zones, respectively. These zones are located farthest from the neutral axis of the beam, which is an imaginary line that divides the beam into equal top and bottom portions. The magnitude of bending stress in a beam is directly proportional to the applied bending moment and inversely proportional to the moment of inertia of the beam's cross-sectional shape.
The moment of inertia is a property that characterizes the beam's resistance to bending. It depends on the shape and dimensions of the beam's cross-section and is calculated differently for different shapes, such as rectangular, circular, or I-beam sections. Bending stress is an important consideration in structural engineering and design, as it determines the strength and structural integrity of beams. Engineers analyze bending stress to ensure that beams are capable of withstanding the applied loads without experiencing excessive deflection or failure.

