Stress
Stress Formula |
||
|
\( \sigma \;=\; \dfrac{ F }{ A_c }\) (Stress) \( F \;=\; \sigma \cdot A_c \) \( A_c \;=\; \dfrac{ F }{ \sigma }\) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \sigma \) (Greek symbol sigma) = Stress | \(lbf \;/\; in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( F \) = Force | \( lbf \) | \(N\) |
| \( A_c \) = Area Cross-section | \( ft^2\) | \( m^2\) |
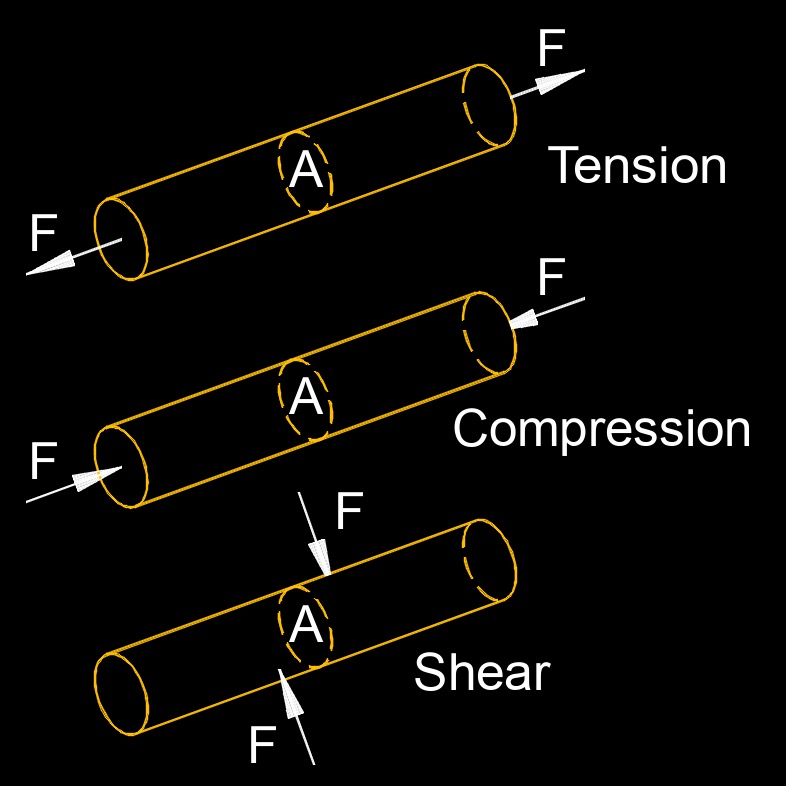
Stress, abbreviated as \(\sigma \) (Greek symbol sigma), also called normal stress, is the force per unit area cross-section. The maximum stress of a material before it breaks is called breaking stress or ultimate tensial stress.
In physics and engineering, stress is the internal force or pressure that acts on a material when it is subjected to external loads or forces. It is a measure of the intensity of the internal forces within a material, which can cause deformation or changes in shape.
Stress is an essential concept in materials science, structural engineering, and mechanics. Understanding the stress behavior of materials is crucial for designing structures, predicting failure points, ensuring safety, and selecting appropriate materials for specific applications. Different materials have different stress limits, known as yield strength, ultimate strength, or breaking strength, beyond which they may experience permanent deformation or failure.

