Orifice Pressure Loss
Orifice Pressure Loss (horizontal orifice and nozzle) formula |
||
| \( \Delta p \;=\; \left( \dfrac{1}{2} \cdot \rho \right) \cdot ( 1 - \beta^4 ) \cdot \left( \dfrac{ Q }{ C_d \cdot A_o \cdot Y } \right)^2 \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \Delta p \) = Pressure lLoss | \(lbf \;/\; in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( \rho \) (Greek symbol rho) = Density | \(lbm \;/\; ft^3\) | \(kg \;/\; m^3\) |
| \( \beta \) (Greek symbol beta) = Ratio of Pipe Inside Diameter to Orifice Diameter | \( dimensionless \) |
\( dimensionless \) |
| \( Q \) = Orifice Flow Rate | \(ft^3 \;/\; sec\) | \(m^3 \;/\; s\) |
| \( C_d \) = Orifice Discharge Coefficient | \( dimensionless \) | \( dimensionless \) |
| \( A_o \) = Orifice Area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( Y \) = Expansion Coefficient (Y = 1 for Incompressible Flow) | \( dimensionless \) | \( dimensionless \) |
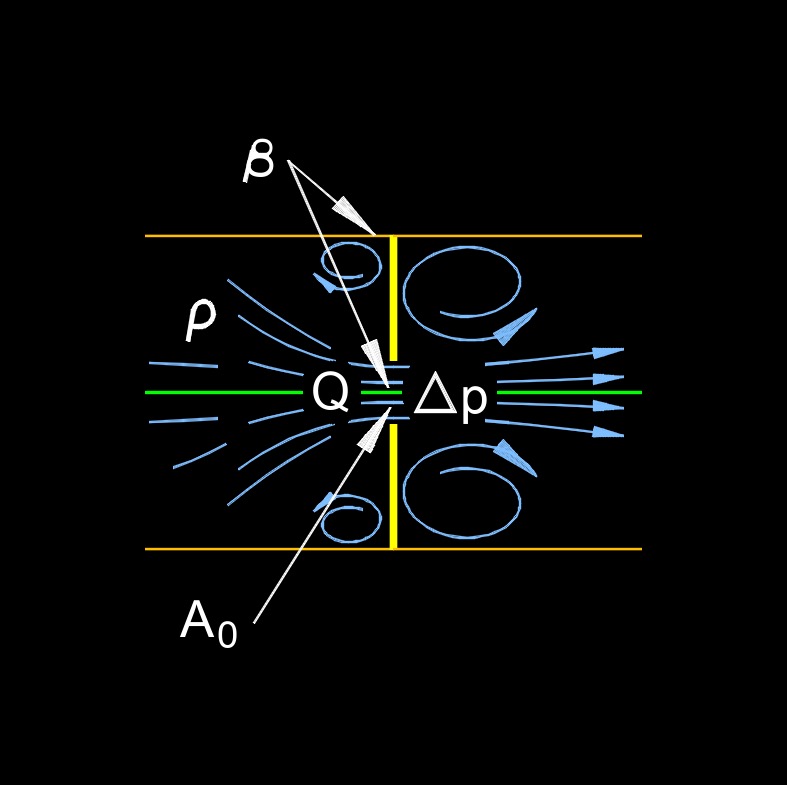 Orifice pressure loss, also called orifice pressure drop or orifice flow, is the decrease in pressure that occurs when a fluid (liquid or gas) passes through a constriction or an orifice in a pipeline, pipe, or other flow system. This phenomenon is commonly encountered in various engineering applications, including fluid mechanics, chemical engineering, and process control.
Orifice pressure loss, also called orifice pressure drop or orifice flow, is the decrease in pressure that occurs when a fluid (liquid or gas) passes through a constriction or an orifice in a pipeline, pipe, or other flow system. This phenomenon is commonly encountered in various engineering applications, including fluid mechanics, chemical engineering, and process control.
The orifice itself is a specifically designed opening or hole in a pipe or plate, typically circular in shape, that is used to control and measure the flow of fluid. When a fluid flows through the orifice, it experiences a change in velocity and pressure. This change in pressure is due to the restriction of the flow area, and it can be used for various purposes, such as regulating flow rates, measuring flow rates, or mixing fluids.
Orifice Pressure Loss vertical orifice and nozzle formula |
||
| \( \Delta p \;=\; \left( \dfrac{1}{2} \cdot \rho \right) \cdot ( 1 - \beta^4 ) \cdot \left( \dfrac{ Q }{ C_d \cdot A_o \cdot Y } \right )^2 - \rho \cdot g \cdot \Delta y \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \Delta p \) = Pressure Loss | \(lbf \;/\; in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( \rho \) (Greek symbol rho) = Density | \(lbm \;/\; ft^3\) | \(kg \;/\; m^3\) |
| \( \beta \) (Greek symbol beta) = Ratio of Pipe Inside Diameter to Orifice Diameter | \( dimensionless \) | \( dimensionless \) |
| \( Q \) = Orifice Flow Rate | \(ft^3 \;/\; sec\) | \(m^3 \;/\; s\) |
| \( C_d \) = Orifice Discharge Coefficient | \( dimensionless \) | \( dimensionless \) |
| \( A_o \) = Orifice Area | \( in^2 \) | \( mm^2 \) |
| \( Y \) = Expansion Coefficient (Y = 1 for Incompressible Flow) | \( dimensionless \) | \( dimensionless \) |
| \( g \) = Gravitational Acceleration | \(ft \;/\; sec^2\) | \(m \;/\; s^2\) |
| \( \Delta y \) = Elvation Change ( \(\Delta y = y_1 - y_2\) ) | \( ft \) | \( m \) |

Orifice Pressure Loss vertical orifice and nozzle formula |
||
| \( Y = C_{d,c} \;/\; C_{d,i} \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( C_{d,c} \) = discharge coefficient compressible fluid | \(lbf \;/\; in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( C_{d,i} \) = discharge coefficient incompressible fluid | \(lbm \;/\; ft^3\) | \(kg \;/\; m^3\) |
| \( \beta \) (Greek symbol beta) = \(d_0 \;/\; d_u\) | \( dimensionless \) | \( dimensionless \) |
| \( d_o \) = orifice or nozzle diameter | ||
| \( d_u \) = upstream pipe inside diameter from orifice or nozzle | ||
