Pressure Drop
Pressure Drop Formula |
||
| \( \Delta P \;=\; \left( \mu \cdot \dfrac{ l }{ d_h } \right) \cdot \left( \rho \cdot \dfrac{ v^2 }{ 2 } \right) \) | ||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( \Delta P \) = Pressure Drop | \(lbf \;/\; in^2\) | \(Pa\) |
| \( \mu \) (Greek symbol mu) = Friction Coefficient | \( dimensionless \) | \( dimensionless \) |
| \( l \) = Pipe Lenght | \( ft \) | \( m \) |
| \( d_h \) = Hydraulic Diameter | \( ft \) | \( m \) |
| \( \rho \) (Greek symbol rho) = Density | \(lbm \;/\; ft^3\) | \(kg \;/\; m^3\) |
| \( v \) = Fluid Velocity | \(ft \;/\; sec\) | \(m \;/\;s\) |
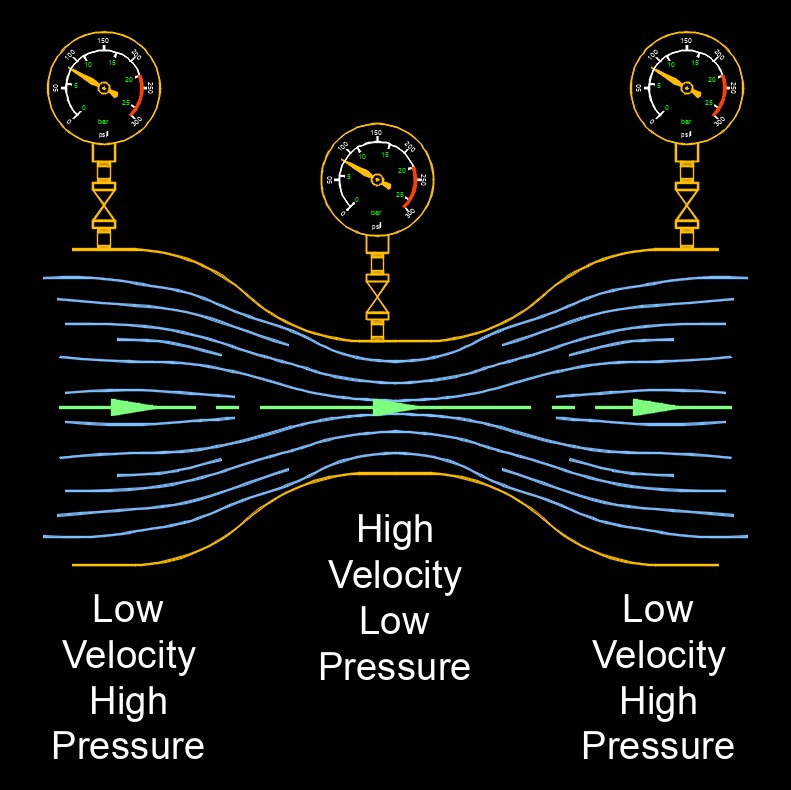
Pressure drop, abbreviated as \(\Delta P\), also called pressure loss, is the difference in pressure between two points, usually caused by friction resistance in the pipe, but moisture can also affect it. It is a common phenomenon in fluid flow systems and can have various causes and implications. Pressure drop typically occurs due to these main factors, frictional loss and localized loss.
Pressure drop is an important consideration in the design, analysis, and operation of fluid flow systems. It affects factors such as flow rate, system efficiency, pump or compressor requirements, and the selection of appropriate pipe sizes and components. Minimizing pressure drop is often desirable to optimize system performance, reduce energy consumption, and ensure adequate pressure levels at critical points in the system. This can be achieved through careful system design, selection of appropriate materials, optimizing flow velocities, and minimizing flow disturbances.
Viscosity - Highly viscous fluids can lead to higher frictional losses, reducing the pressure in the system.
Pipe Size - Inadequate pipe diameter can lead to increased fluid velocity, resulting in higher frictional losses.
Corrosion and Scaling - Accumulation of deposits or corrosion inside the pipes reduces the effective diameter, increasing friction and causing pressure drop.
Temperature Changes - Changes in fluid temperature can affect its viscosity, density, and other properties, leading to variations in pressure drop.
Pipe Material - The material of the pipe can impact the roughness and, consequently, the frictional losses.
Leaks - Any leakage in the piping system results in a direct loss of fluid and pressure.
Pump Performance - Inadequate pump performance or improper pump sizing can lead to insufficient pressure generation.
System Design - Poorly designed systems with improper layouts or inadequate consideration of flow dynamics can result in pressure drop.

