Solid Geometry
Mathematics, Solid Prism, Solid Pyramid, Solid Wedge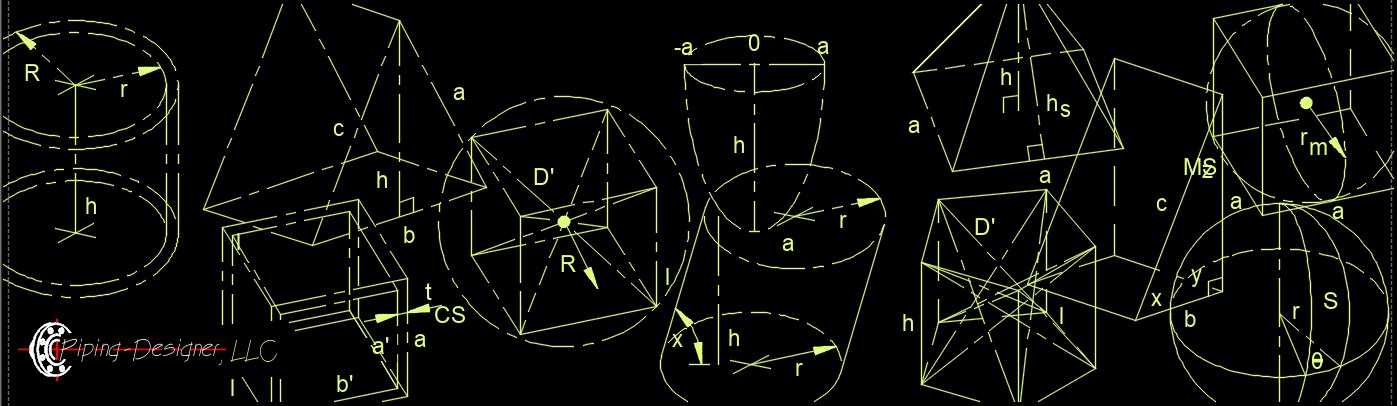 Solid geometry, also known as three-dimensional geometry, is a branch of mathematics that deals with the properties and relationships of three-dimensional objects, such as cubes, spheres, cylinders, cones, and pyramids. It is a fundamental area of study in mathematics and has many practical applications in fields such as engineering, architecture, physics, and computer graphics. Solid geometry builds on the concepts of plane geometry, extending them to three dimensions. Solid geometry plays a crucial role in many areas of science, engineering, and technology, including computer-aided design (CAD), architecture, and physics. It provides a foundation for understanding the geometry of the physical world around us and is essential for solving many practical problems in a wide range of fields.
Solid geometry, also known as three-dimensional geometry, is a branch of mathematics that deals with the properties and relationships of three-dimensional objects, such as cubes, spheres, cylinders, cones, and pyramids. It is a fundamental area of study in mathematics and has many practical applications in fields such as engineering, architecture, physics, and computer graphics. Solid geometry builds on the concepts of plane geometry, extending them to three dimensions. Solid geometry plays a crucial role in many areas of science, engineering, and technology, including computer-aided design (CAD), architecture, and physics. It provides a foundation for understanding the geometry of the physical world around us and is essential for solving many practical problems in a wide range of fields.
- See Articles - List of Tags, List of Categories, List of Articles, List of Glossaries, Nomenclature and Symbols
Plane Geometry
Some Concepts in Solid Geometry
- The volume and surface area of various three-dimensional shapes and figures
- The properties of prisms, such as the rectangular prism and triangular prism
- The properties of pyramids, such as the square pyramid and triangular pyramid
- The properties of cylinders, cones, and spheres, including formulas for their volumes and surface areas
- The use of coordinate geometry to describe the location and properties of points, lines, and shapes in three-dimensional space.
Solid Geometry Classification
- Polyhedron - Is a solid with no curved edges or sides.
- Solid Prism - Prisms are solids with two congruent parallel polygon ends that are exactly the same.
- Oblique prism - Has with both bases not alligned above each other and the center not at 90° to the other base center.
- Right prism - Has both bases directly above each other and having the centers at 90° to each others base.
- Cube - Is a regular polyhedron with square faces.
- Right Hexagonal Prism - Has hexagonal bases and each face is a regular polygon with equal sides and equal angles.
- Right Octagonal prism -
- Right Pentagonal Prism - Has pentagonal bases and each face is a regular polygon with equal sides and qual angles.
- Right Rectangular Prism - Has six faces that are rectangles with equal sides and equal angles.
- Right Square Prism - Has square bases, four faces that are rectangles with equal sides and equal angles.
- Right Triangular prism -
- Solid Pyramid - Pyramids are solids with one polygon base and lateral faces that taper to an apex.
- Oblique Pyramid - The apex is not alligned above the center at 90° to the base.
- Right Pyramid - The apex is directly above the center at 90° to the base.
- Right Pentagonal Pyramid - Has a pentagon base and the apex alligned above the center of the base.
- Right Square Pyramid - Has a square base and the apex alligned above the center of the base.
- Right Triangular Pyramid - Has a triangle base and the apex alligned above the center of the base.
- Solid Wedge - Wedges have two triangle ends and three polygon sides.
- Isosceles Triangle Wedge - Has three rectangle sides and two isoscelees triangle sides.
- Right Triangle Wedge - Has two right triangle ends and three rectangle sides.
- Solid Prism - Prisms are solids with two congruent parallel polygon ends that are exactly the same.
- Non-polyhedron - Is a solid with curved edges or sides.
- Cone - Cones have one circular base tapering to an apex.
- Oblique Cone - The apex is not alligned above the center at 90° to the base.
- Right Cone - Has a circle base with the apex alligned at 90° above the center of the base.
- Cylinder - Cylinders have two circular parallel congruent bases.
- Oblique Cylinder - Both bases not alligned above each other and the center not at 90° to the other base center.
- Right Cylinder - Both bases direictly above each other and having the centers at 90° to each others base.
- Right Elliptic Cylinder - No parallel lines and both bases are ellipses.
- Right Hollow Cylinder - A hollow core with both bases direictly above each other and having the center at 90° to each others base.
- Ellipsoid - Ellipsoids have a spherical like shape with an ellipse cross section.
- Paraboloid -
- Elliptic Paraboloid - Has a u-shaped curve with an elliptical base.
- Sphere - All points equally spaces from a given point of a three dimensional solid.
- Torus - Is shaped like a donut.
- Cone - Cones have one circular base tapering to an apex.

