Plane Geometry
Triangle, Structural Steel, Mathematics, Quadrilateral, Ellipse, Circle, Solid Geometry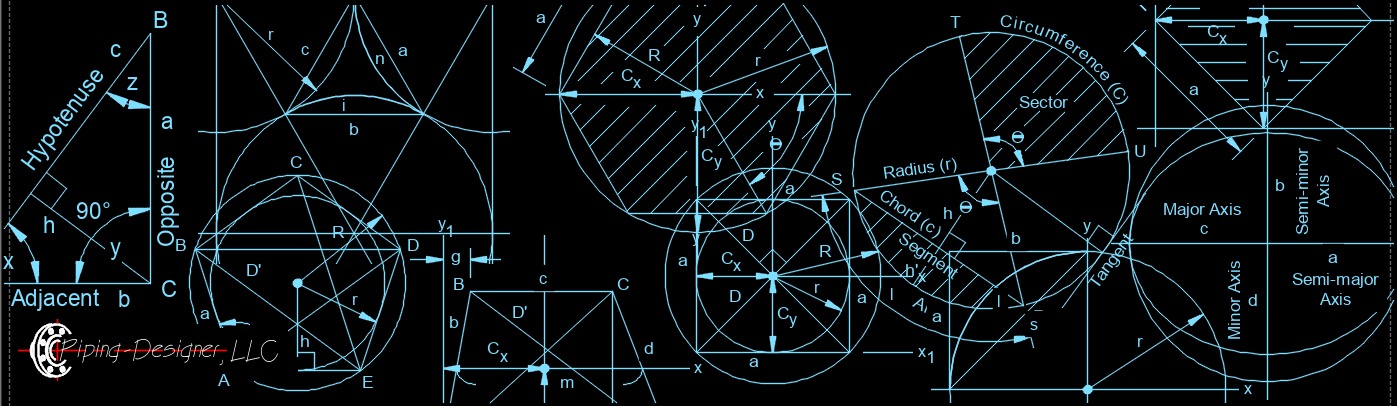 Plane geometry, also known as two-dimensional geometry, is a branch of mathematics that focuses on the properties and relationships of points, lines, angles, and shapes in a two-dimensional plane. It is a fundamental area of study in mathematics and has many practical applications in fields such as engineering, architecture, physics, and computer graphics. Plane geometry begins with basic concepts such as points, lines, and planes, and then progresses to more complex topics such as angles, triangles, polygons, circles, and conic sections. The study of plane geometry involves the use of axioms and postulates to prove theorems and derive formulas that describe the properties and relationships of various geometric shapes and figures. Overall, plane geometry provides a foundation for understanding the geometry of the physical world around us and plays a crucial role in many areas of science, engineering, and technology.
Plane geometry, also known as two-dimensional geometry, is a branch of mathematics that focuses on the properties and relationships of points, lines, angles, and shapes in a two-dimensional plane. It is a fundamental area of study in mathematics and has many practical applications in fields such as engineering, architecture, physics, and computer graphics. Plane geometry begins with basic concepts such as points, lines, and planes, and then progresses to more complex topics such as angles, triangles, polygons, circles, and conic sections. The study of plane geometry involves the use of axioms and postulates to prove theorems and derive formulas that describe the properties and relationships of various geometric shapes and figures. Overall, plane geometry provides a foundation for understanding the geometry of the physical world around us and plays a crucial role in many areas of science, engineering, and technology.
Solid Geometry
Some Concepts in Plane Geometry
- Parallel lines and their relationship to angles and transversals
- Congruent and similar figures
- Properties of triangles, such as the Pythagorean theorem, and the relationship between angles and side lengths
- Properties of circles, such as the relationship between angles, arcs, and chords
- The use of coordinate geometry to describe the location and properties of points, lines, and shapes on a plane.
Plane Geometry Classification
- Circle - All points are at a fixed equal distance from a center point.
- 2 Overlapping Circle - Two overlapping circles with equal length arcs connecting at the vertices.
- 3 Overlapping Circle - Equal length arcs connecting at the vertices of three overlapping circles.
- 3 Connecting Circle - Three equal length arcs connecting at the vertices bound by circles.
- 4 Connecting Circle - Four equal length arcs connecting at the vertices bound by circles.
- Annulus of a Circle - The area between two concentric circle
- Arc Length of a Circle - A sector is a fraction of the area of a circle.
- Area of a Circle -
- Chord of a Circle - An angle formed by a chord and a tangent that intersect on a circle is half the measure of the intercepted arc.
- Circle Corner - A right triangle having acute vertices on a circle with the hypotenuse outside the circle.
- Circumference of a Circle - The total length of the boundary or perimeter of the circle. It is the distance you would travel if you were to walk around the circle.
- Diameter of a Circle - A circle is any straight line segment that passes through the center of the circle and whose endpoints are on the circle.
- Distance from the Centroid of a Circle - The distance between the centroid (the geometric center) of the circle and a given point, either inside, on, or outside the circle. The centroid of a circle is simply its center, as a circle is a perfectly symmetric shape, and its centroid coincides with the point at the center of the circle.
- Elastic Section Modulus of a Circle - A geometric property used in structural engineering to calculate the maximum stress in a circular cross-section under bending.
- Half Circle - Half of the interior of a circle having a straight chord and an arc.
- Hollow Circle - Two circles each having all points on each circle at a fixed equal distance from a center point.
- Plastic Section Modulus of a Circle - A measure used in structural engineering to describe the capacity of the section to resist plastic bending.
- Polar Moment of Inertia of a Circle - A measure of its resistance to torsional deformation.
- Quarter Circle - A part of the interior of a circle having two radius boundries at a 90° angle and an arc.
- Radius of a Circle - A line segment between the center point and a point on a circle or sphere.
- Radius of Gyration of a Circle - About its center (perpendicular to its plane) is a measure of how its mass is distributed relative to the axis of rotation.
- Second Moment of Area of a Circle - Its resistance to bending or deflection about a given axis. It's a geometric property that depends on the distribution of the area of the circle relative to that axis.
- Sector of a Circle - A part of the interior of a circle having two radius boundries and an arc.
- Segment of a Circle - An interior part of a circle bound by a chord and an arc.
- Thin Wall Circle - Two circles each having all points on each circle at a fixed equal distance from a center point.
- Torsional Constant of a Circle - A measure of its resistance to torsion (twisting).
- Ellipse - A two-dimensional figure with a conic section or a stretched circle.
- Catenary Curve - Has a u-shaped curve and can be represented by a hanging chain or cable under its own weight and supported only at it's ends.
- Foci of an Ellipse - A point used to define the conic section.
- Hollow Ellipse - Two ellipses with a conic section or a stretched circle.
- Sector of an Ellipse - A part of the interior of an ellipse having two radius boundries and an arc.
- Segment of an Ellipse - An interior part of a ellipse bound by a chord and an ellipse.
- Semi-major and Semi-minor Axis of an Ellipse - The semi-major axis and the semi-minor axis are two important parameters that characterize the size and shape of an ellipse.
- Polygon - A closed plane figure for which all edges are line segments and not necessarly congruent.
- Concave Polygon - A polygon where one or more angles are greater than 180° and some vertices point inward.
- Convex Polygon - A a polygon where all interior angles are less than 180° and all vertices point outward.
- Irregular Polygon - A polygon where all edge and angles are not the same. It can be concave or convex.
- Regular Polygon - A polygon where all edges are congruent and all angles are congruent.
- Self-intersecting Polygon - A polygon where one or more edges cross over another.
- Rectangle - A quadrilateral with two pair of parallel edges.
- Square - A quadrilateral with four equal side lengths and 90° interior angles.
- Triangle - A polygon with three sides, three vertices, and three angles. The sum of the interior angles of any triangle is always 180 degrees.
- Acute Triangle - Has three angles less than 90°.
- Equilateral Triangle - Has three edges that are the same length and all edges and angles are congruent.
- Isosceles Triangle - Has two edges that are the same length or at least two congruent edges.
- Oblique Triangle - Is tilted at an angle, not horizontal or vertical.
- Obtuse Triangle - Has one of the three angles more than 90°.
- Right Isosceles Triangle - Has one edge a right 90° interior angle and the other two angles are 45°.
- Right Triangle - Has one edge a right 90° interior angle.
- Scalene Triangle - All three edges are different lengths and all three angles are different angles.
- Quadrilateral - A polygon with four sides, four vertices, and four angles. The sum of the interior angles of a quadrilateral is always 360 degrees. Quadrilaterals can have various shapes and properties, and they are classified into different types based on their characteristics.
- Acute Trapezoid - A trapezoid has two adjacent acute angles on its longer base edge.
- Isosceles Trapezoid - A trapezoid with only one pair of parallel edges and having base angles that are the same.
- Kite - A quadrilateral with two pairs of adjacent edges that are congruent.
- Obtuse Trapezoid - A trapezoid with one acute and one obtuce angle on each base.
- Parallelogram - A quadrilateral with two pairs of parallel opposite edges.
- Rectangle - A quadrilateral with two pair of parallel edges.
- Rhombus - A parallelogram with four congruent edges.
- Right Trapezoid - A trapezoid with only one pair of parallel edges and two adjacent right angles.
- Rounded Corner Rectangle - A quadrilateral with two pair of parallel edges and rounded corners.
- Self-intersecting Rectangle - One edge crosses over another.
- Square - A quadrilateral with four equal edge lengths and 90° interior angles.
- Trapezoid - A quadrilateral that has a pair of parallel opposite edges.
- Tri-equilateral Trapezoid - A trapezoid with only one pair of parallel edges and having base angles that are the same with three congruent edges.
- Pentagon - A polygon with 5 edges.
- Regular Pentagon - A polygon with 5 congruent edges.
- Hexagon - A polygon with 6 edges.
- Regular Hexagon - A polygon with 6 congruent edges.
- Heptagon - A polygon with 7 edges.
- Regular Heptagon - A polygon with 7 congruent edges.
- Octagon - A polygon with 8 edges.
- Nonagon - A polygon with 9 edges.
- Decagon - A polygon with 10 edges.
- Hendecagon - A polygon with 11 edges.
- Dodecagon - A polygon with 12 edges.
- Triskaidecagon - A polygon with 13 edges.
- Tetrakaidecagon - A polygon with 14 edges.
- Pentadecagon - A polygon with 15 edges.
- Hexakaidecagon - A polygon with 16 edges.
- Heptadecagon - A polygon with 17 edges.
- Octakaidecagon - A polygon with 18 edges.
- Enneadecagon - A polygon with 19 edges.
- Icosagon - A polygon with 20 edges.
- Triacontagon - A polygon with 30 edges.
- Tetracontagon - A polygon with 40 edges.
- Pentacontagon - A polygon with 50 edges.
- Hexacontagon - A polygon with 60 edges.
- Heptacontagon - A polygon with 70 edges.
- Octacontagon - A polygon with 80 edges.
- Enneacontagon - A polygon with 90 edges.
- Hectogon - A polygon with 100 edges.
- Chiliagon - A polygon with 1,000 edges.
- Myriagon - A polygon with 10,000 edges.
Geometric Properties of Structural Shapes
- Cross
- Hollow Rectangle
- Rectangular Angle
- Rotating Rectangle
- Square Angle
- Square Channel
- Square Diamond
- Square I Beam
- Square T Beam
- Tapered Channel
- Tapered I Beam
- Tapered T Beam
- Thin Wall Rectangle
- Unequal I Beam
- Zed

