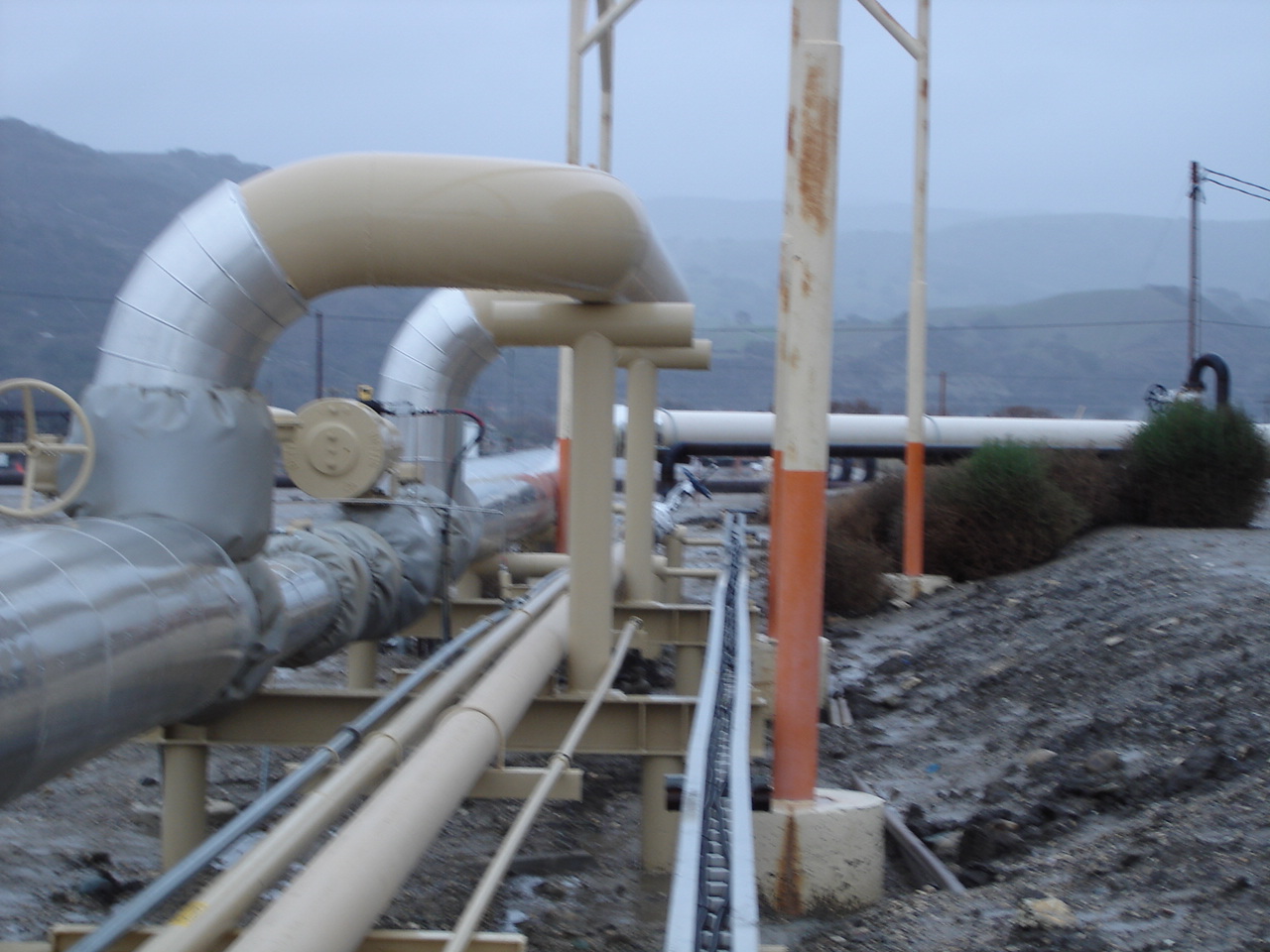
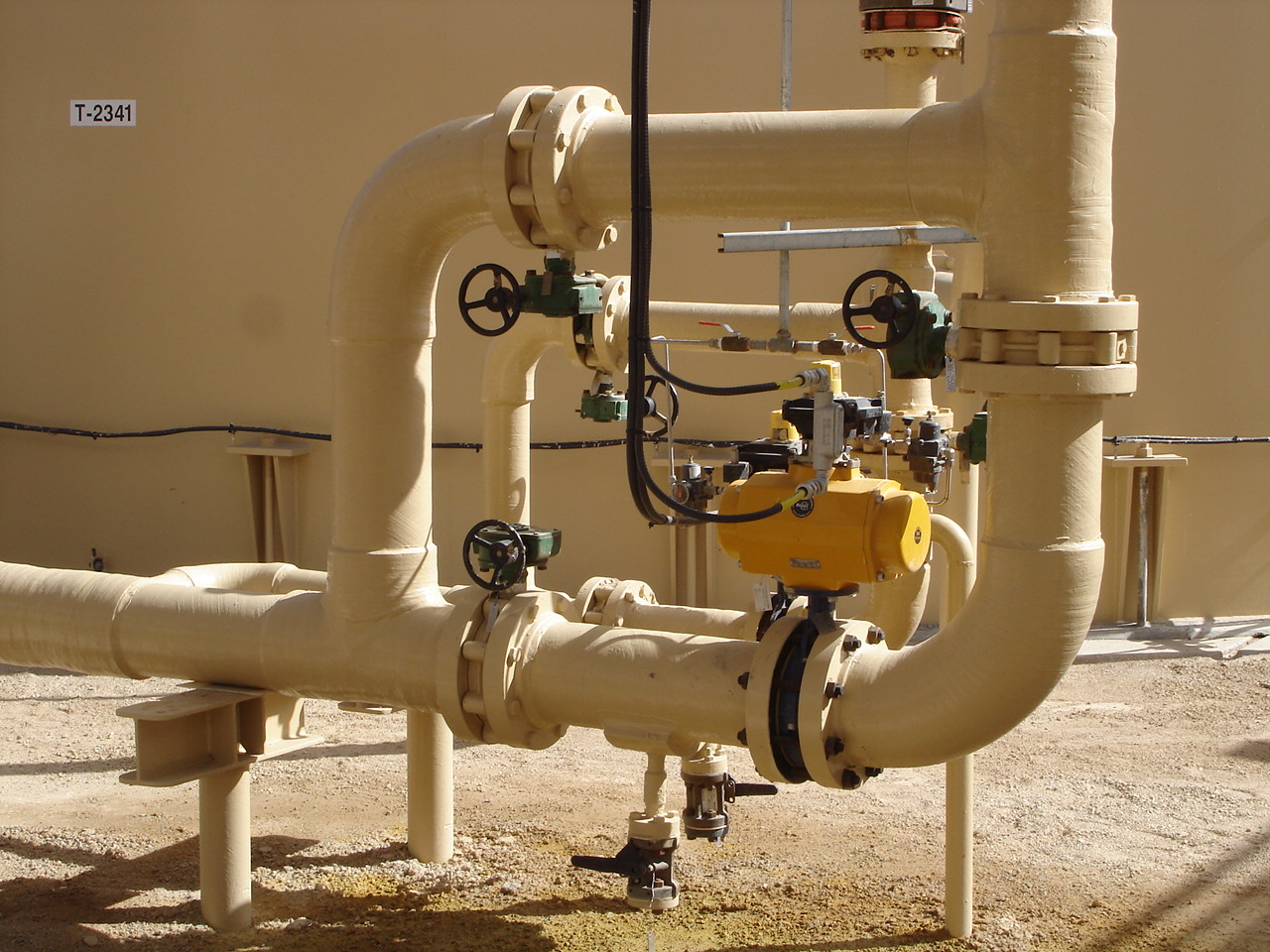
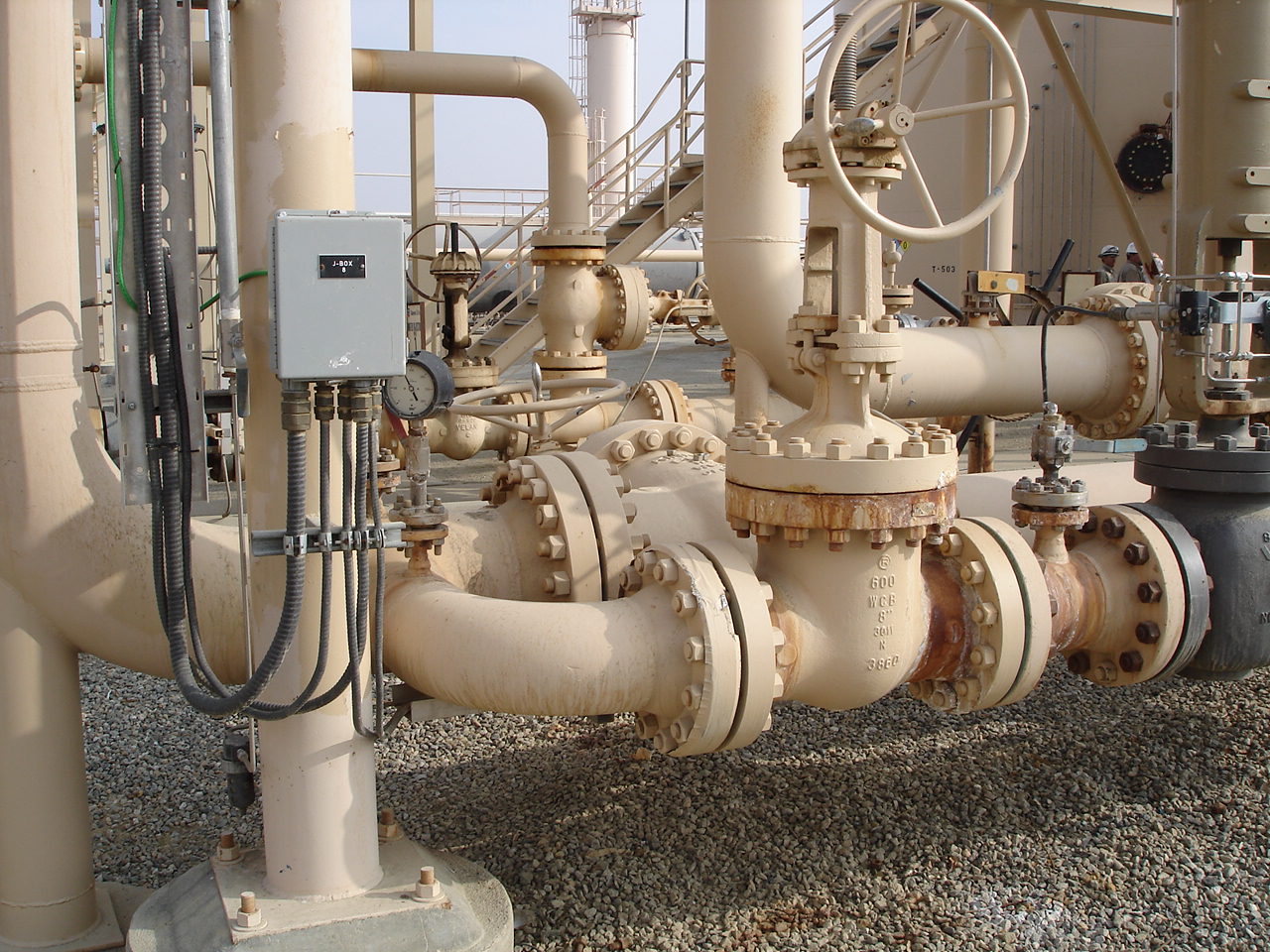
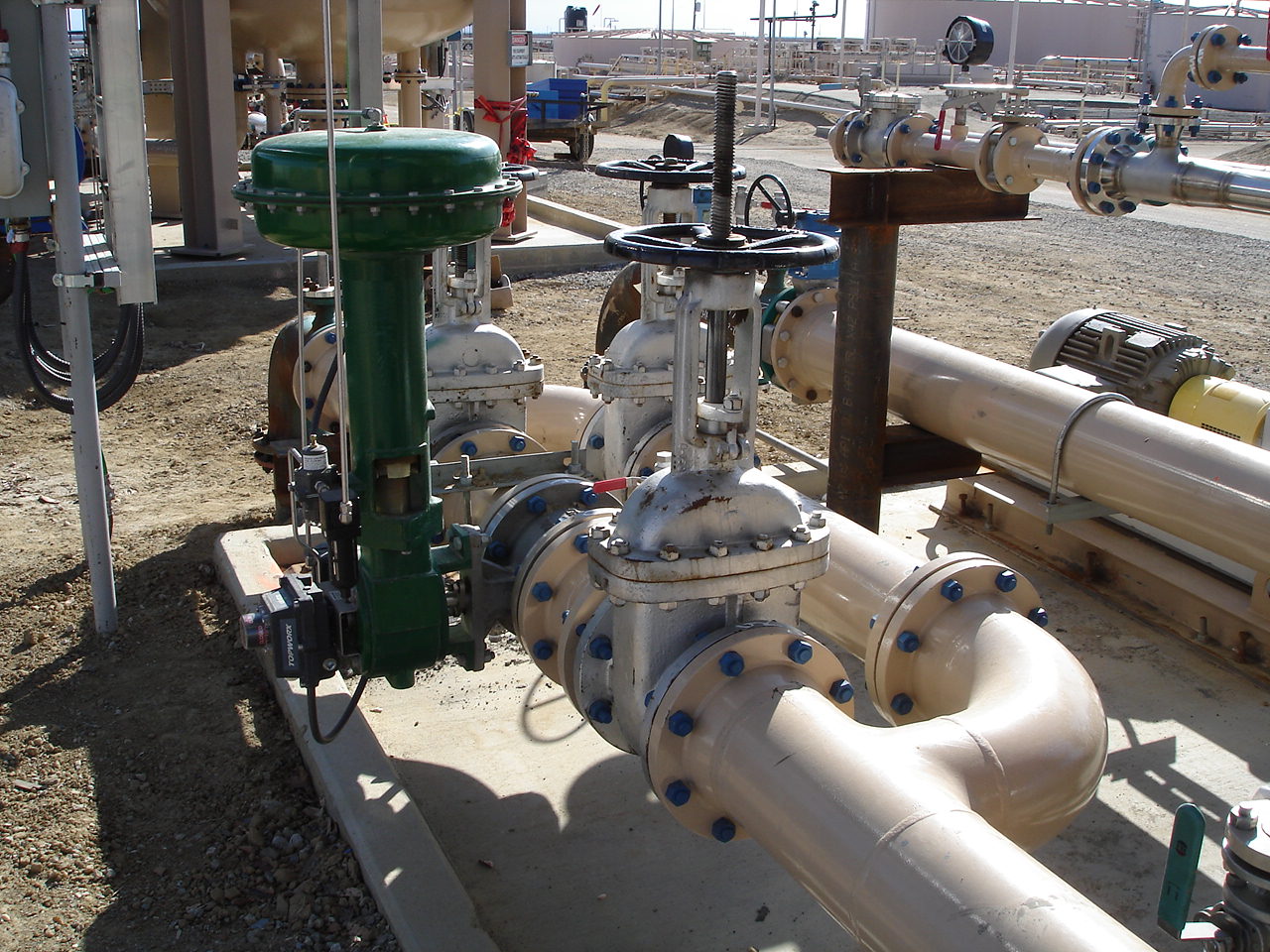
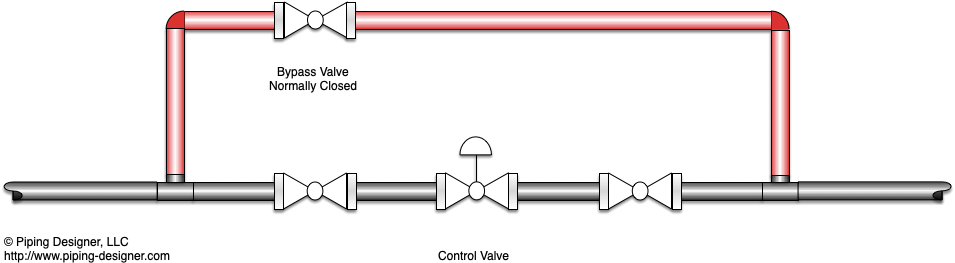
Bypass Loop
Bypass loop, also called a bypass line or bypass pipe, is a series of pipe, valves and fittings that allow for a valve, instrument or piece of equipment to be bypassed. Most bypass loops are installed to allow for continuious operation of a facility while maintenance is being performed. It is a secondary piping arrangement that diverts flow around a primary component or system. The purpose of a bypass loop is to provide an alternative pathway for fluid, gas, or other substances in case the primary component needs maintenance, repair, or adjustment. It essentially allows for temporary isolation of the primary component without disrupting the overall operation of the system.
Bypass Loops Applications
Control Systems - Bypass loops can be used in control systems to regulate flow rates or pressure, ensuring that the system operates within specified parameters.
Control Valves - A bypass loop is installed to allow for removing the valve from service for maintenence or for calibrating a positioner or actuator to ensure the valve continues to operate as intended. A control valve has a couple different options for the bypass valve. If the process is at steady state, the designer may opt to include a globe valve or some other type of valve that can help control pressure or flow across the valve.
Equipment - Bypass loops for equipment may not always depend on downtime for maintenance. Some heat exchangers may be bypassed when not in use to prevent fouling. As temperatures begin to go out of specification, the exchangers may be brought online. Sometimes upstream conditions are such that a water softener may not be necessary. In-line gas filters and liquid-gas separators will eventually need to have their elements changed or replaced. A bypass loop will allow for the filter to be bypassed while the elements are replaced.
HVAC Systems - Bypass loops can be part of HVAC systems to regulate flow and temperature. They might be used to balance the distribution of air or fluid in different parts of a building.
Industrial Processes - In manufacturing or chemical processing, a bypass loop can be used to divert flow around a piece of equipment, such as a filter, pump, or heat exchanger, for cleaning or maintenance without interrupting the production process.
Instrumentation - Some types of flow meters require periodic maintence to ensure they are working properly Inline meters, such as coriolis, magnetic flow meters and orifice plates may need to be taken offline for troubleshooting. If the meter is a master meter, it may need to be removed from service to be calibrated.
Pipelines - In pipeline systems, bypass loops can be used to redirect flow in case of a blockage or a damaged section of the pipeline.
Water Treatment - Bypass loops can be used in water treatment facilities to redirect water flow around treatment units, allowing for maintenance or repairs to be performed on one unit while keeping the overall system operational.
Bypass loops are designed to be versatile and flexible. They are equipped with valves, pumps, and other control elements to allow for the diversion of flow as needed. Proper design and installation of bypass loops are crucial to ensure that they effectively serve their purpose while maintaining system efficiency and safety. When designing or working with bypass loops, it's important to consider factors such as flow rates, pressure drops, valve selection, control mechanisms, and potential safety risks to ensure that the bypass system functions as intended and provides a reliable solution for maintenance or system adjustments.
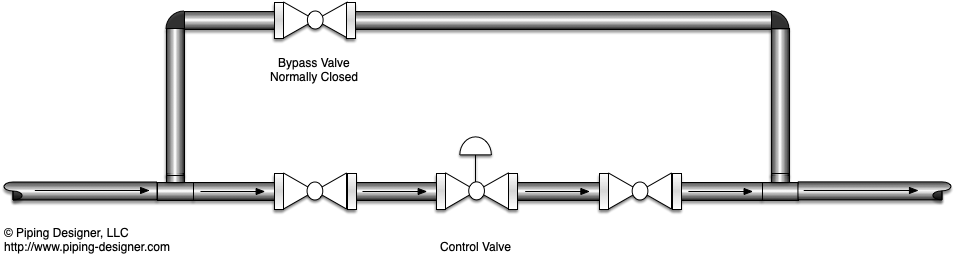 Piping Bypass Loop
Piping Bypass Loop 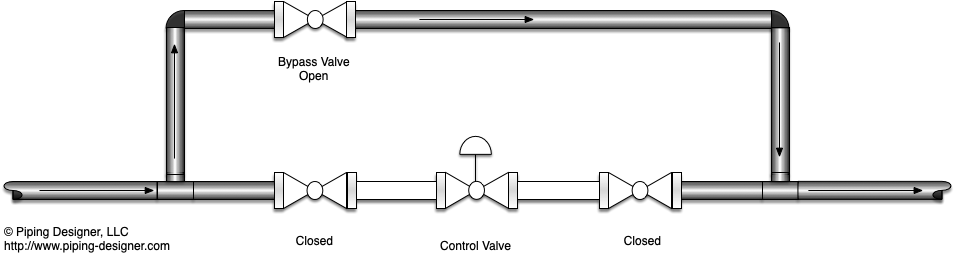 Piping Bypass Loop Open
Piping Bypass Loop Open
Bypass Loop Considerations
A challenge for any operator is how to design a bypass loop without creating a deadleg in the system. For services that are corrosive, having zero flow through a portion of the pipe will increase the rate at which corrosion forms. As shown in the figure below, when the bypass valve is closed, there is a portion of the pipe that remains stagnent. While the loop can be reconfigured several different ways, it is difficult to design a loop which does not create a dead leg.