Buoyancy Mass
Buoyancy Mass Formula |
||
|
\( m_b \;=\; m_o \cdot \left( 1 - \dfrac{\rho_f }{ \rho_o} \right) \) (Buoyancy Mass) \( m_o \;=\; \dfrac{ m_b }{ 1 - \dfrac{ \rho_f }{ \rho_o } } \) \( \rho_f \;=\; - \rho_o \cdot \dfrac{ m_b }{ m_o } - 1 \) \( \rho_o \;=\; \dfrac{ 1 }{ 1 - \dfrac{ m_b }{ m_o } } \cdot \rho_f \) |
||
| Symbol | English | Metric |
| \( m_b \) = Buoyancy Mass | \( lbm \) | \(kg\) |
| \( m_o \) = True Vacuum Mass of the Object | \( lbm \) | \(kg\) |
| \( \rho_f \) (Greek symbol rho) = Surrounding Fluid Density | \(lbm \;/\; ft^3\) | \(kg \;/\; m^3\) |
| \( \rho_o \) (Greek symbol rho) = Object Density | \(lbm \;/\; ft^3\) | \(kg \;/\; m^3\) |
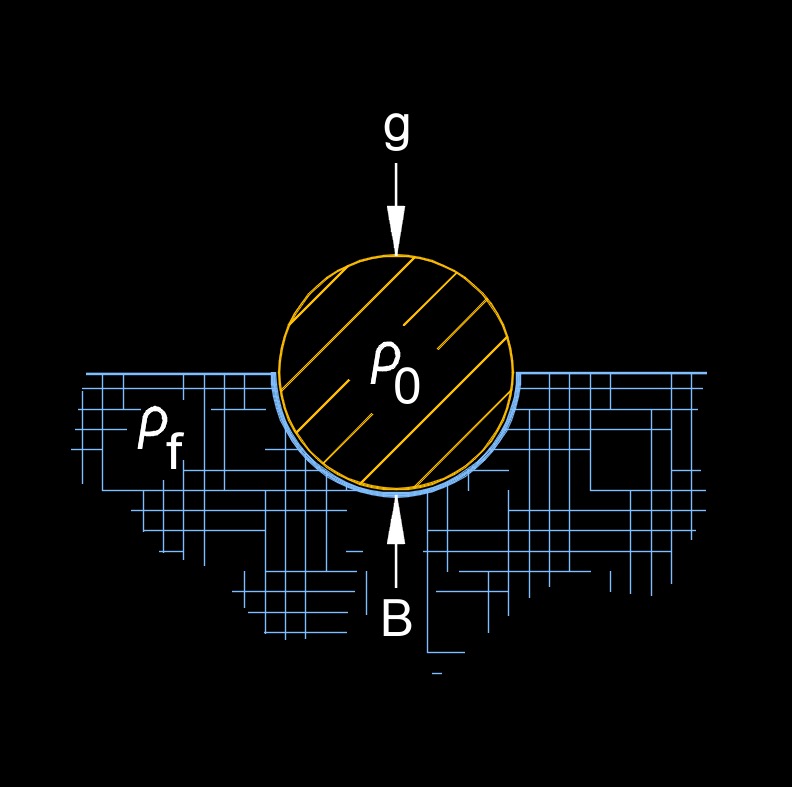 Buoyancy mass, abbreviated as \(m_b\), also called apparent mass, is the apparent increase in the mass of an object when it is submerged in a fluid. It is the difference between the actual mass of the object and the mass of the fluid displaced by the object. This apparent increase in mass is due to the buoyant force acting on the object, which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. The buoyancy mass is equal to the ratio of the buoyant force acting on the object to the acceleration due to gravity. You could also say buoyancy mass is the amount of matter an object has relative to the density of the liquid.
Buoyancy mass, abbreviated as \(m_b\), also called apparent mass, is the apparent increase in the mass of an object when it is submerged in a fluid. It is the difference between the actual mass of the object and the mass of the fluid displaced by the object. This apparent increase in mass is due to the buoyant force acting on the object, which is equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object. The buoyancy mass is equal to the ratio of the buoyant force acting on the object to the acceleration due to gravity. You could also say buoyancy mass is the amount of matter an object has relative to the density of the liquid.

